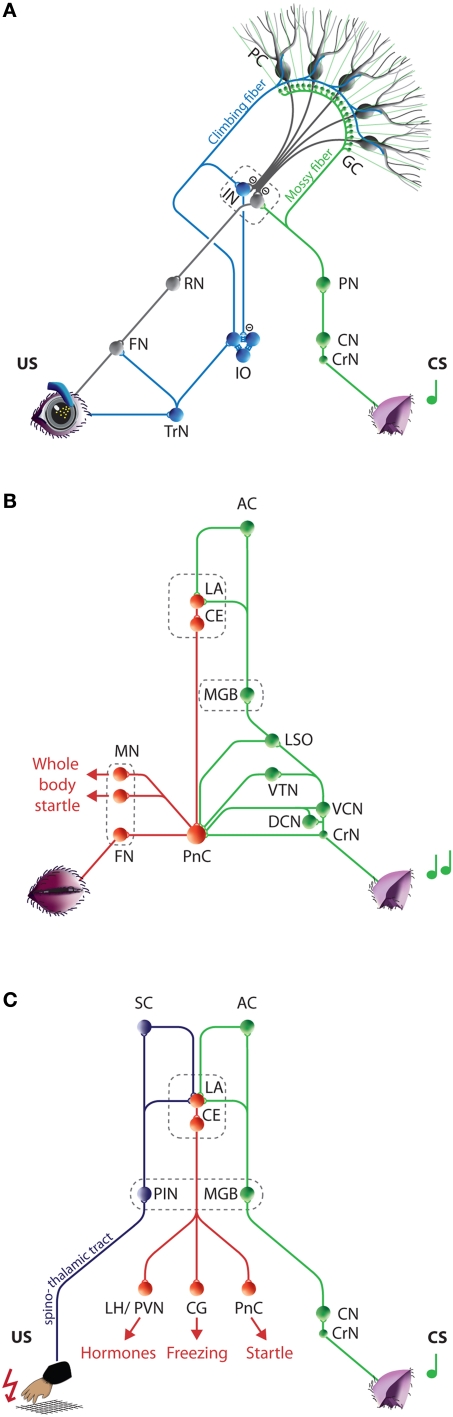
Figure 1.
Neurocircuitries underlying eyeblink conditioning, auditory startle reflexes, and cued fear conditioning. (A) Neural circuits engaged during eyeblink conditioning. The mossy fiber CS-pathway (green) and climbing fiber US-pathway (blue) converge at the PCs in the cerebellar cortex and to a much lesser extent at the IN neurons. The CR-pathway (gray) is formed by the cerebellar output neurons and relayed via the RN to the FN and OMN, which innervate the eyelid muscles. (For simplicity only the eyelid innervation by the FN is depicted, see text for more details.) Conditioned induced plasticity at the PC and possibly also in the IN gradually leads to the establishment of an adequate CR. (B) Neural circuits engaged during auditory startle reflexes. The fastest route for transmission of acoustic input into motor output is from the CrN via the PnC to the motor neurons, including the FN. In addition, multiple afferent systems including the LSO, VTN, DCN, and VCN excitate the giant PnC neurons. Amygdala activity directly controls the expression of the startle reflex by its projections to the PnC. (C) Neural circuits engaged during cued fear conditioning. The tone (CS) and electric foot shock (US) are relayed to the LA from thalamic and cortical regions of the auditory (green) and somatosensory (purple) systems, respectively. The LA directly and indirectly projects to the CE, which efferents (red) control the expression of the different aspects of the fear reaction. One or two paired trials induces efficient plasticity in the LA resulting in typical fear CRs including freezing, tachycardia, tachypneu, and facial responses. AC, Auditory cortex; CE, Central amygdala; CG, Central gray; CN, Cochlear nucleus; CrN, Cochlear root nucleus; CS, Conditioned stimulus; DCN, Dorsal cochlear nucleus; FN, Facial nucleus; GC, Granule cell; IN, Interposed nuclei; IO, Inferior olive; LA, Lateral amygdala; LH, Lateral hypothalamus; LSO, Lateral superior olive; MGB, Medial geniculate body of the thalamus; MN, Motor neurons; OMN Oculomotor Nucleus, PC, Purkinje cell; PIN, Posterior intralaminar nucleus of the thalamus; PN, Pontine nuclei; PnC, Caudal pontine reticular nucleus; PVN, Paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus ; RN, Red nucleus; SC, Somatosensory cortex; TrN, Trigeminal nerve nucleus; US, Unconditioned stimulus; VCN, Ventral cochlear nucleus; VTN, Ventrolateral tegmental nucleus.