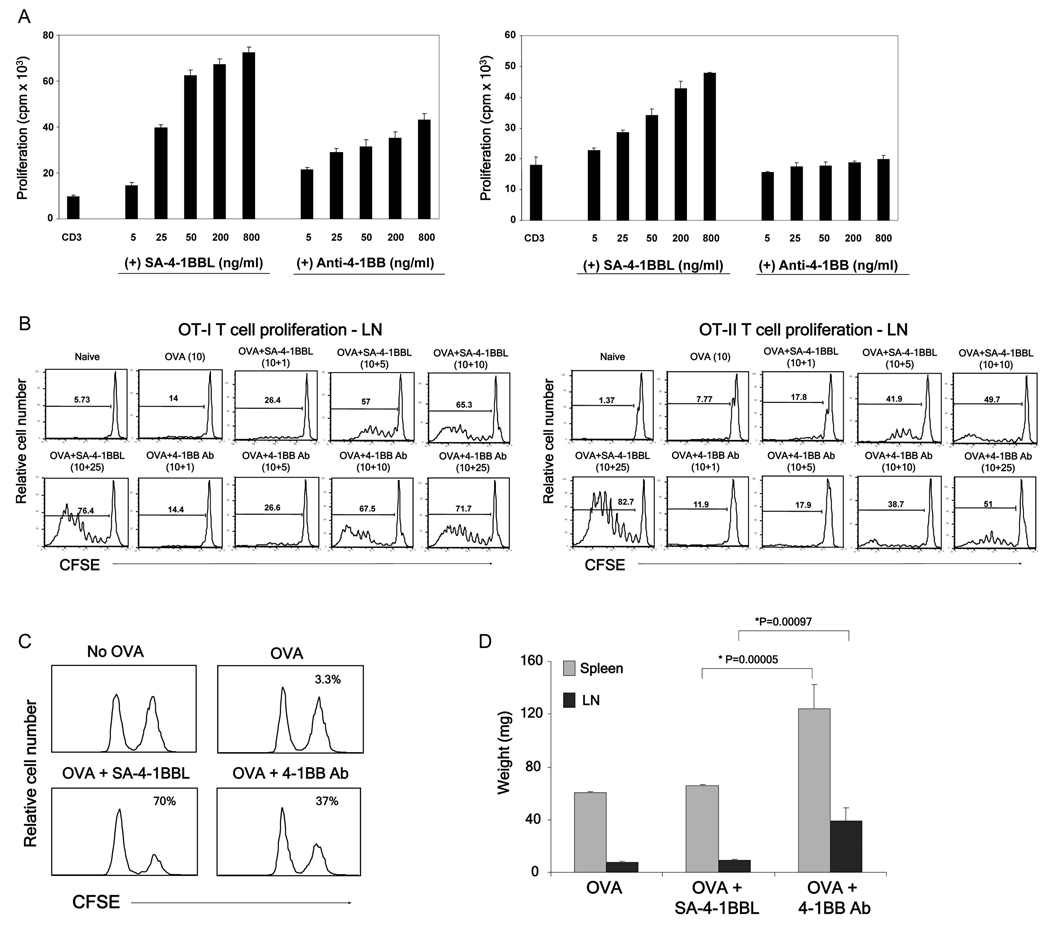
Fig 1.
SA-4-1BBL demonstrates better immune activity than an agonistic anti-4-1BB Ab without Ab-associated toxicity. (A) In vitro CD8+ T cell (left) and CD4+ T cell (right) proliferation. Flow sorted CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were stimulated for 3 days with a suboptimal dose of an agonistic anti-CD3 Ab in conjugation with various doses of SA-4-1BBL or 3H3 Ab in the presence of irradiated syngeneic splenocytes. Cells were pulsed with [3H]-thymidine for the last 16 hrs of culture. (B) In vivo OT-I and OT-II T cell proliferation. One million flow sorted OT-I T cells and OT-II (CD45.2+) were labeled with CFSE and injected i.v. into naïve congenic C57BL/6.SJL (CD45.1+) mice. Mice were vaccinated i.v. with OVA (10 µg) in combination with various doses (µg) of SA-4-1BBL or 3H3 Ab as indicated. Proliferation was assessed using multiparameter flow cytometry 3 days after vaccination. (C) In vivo killing response. C57BL/6 mice were immunized i.v. with OVA (50 µg) in combination with 3H3 Ab (25 µg) or SA-41BBL (25 µg). Seven days post vaccination, mice received SIINFEKL-pulsed syngeneic splenocytes and peptide-specific killing was assessed 2 days later and expressed as percent lysis for each histogram. (D) In vivo toxicity as assessed by the weight of spleen and lymph nodes harvested from mice vaccinated in panel C. p values determined by Student’s t test. Data are representative of a minimum of three independent experiments for Panels A–C.