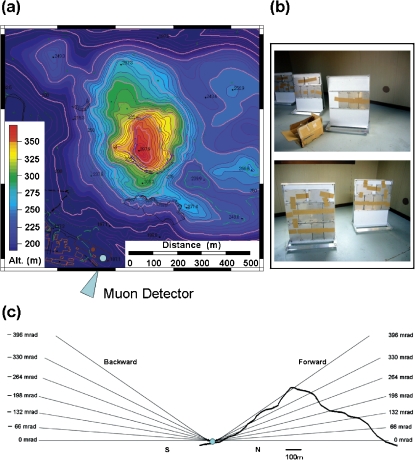
Fig. 5.
(a) Topography of the 1944 Usu lava dome and the location of the cosmic-ray muon detector (arrow). (b) The photographs of the nuclear emulsion photographic films protected by steel plates. (c) The cross-section of the lava dome showing geometrical configurations used in the present measurements. The data of muons arriving from the backward direction are also used to confirm the detection efficiency.