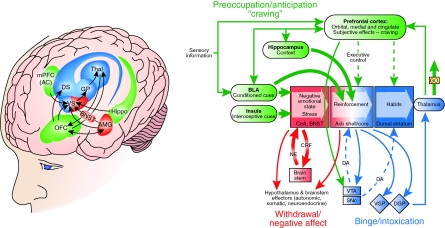
Figure 5.
Neurocircuitry schematic illustrating the combination of neuroadaptations in the brain circuitry for the three stages of the addiction cycle that promote drug-seeking behavior in the addicted state. Note the activation of the ventral striatum/dorsal striatum/extended amygdala driven by cues through the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala and stress through the insula. The frontal cortex system is compromised, producing deficits in executive function and contributing to the incentive salience of drugs compared to natural reinforcers. Dopamine systems are compromised, and brain stress systems such as CRF are activated to reset further the salience of drugs and drug-related stimuli in the context of an aversive dysphoric state (modified with permission from Koob et al, 2008a).