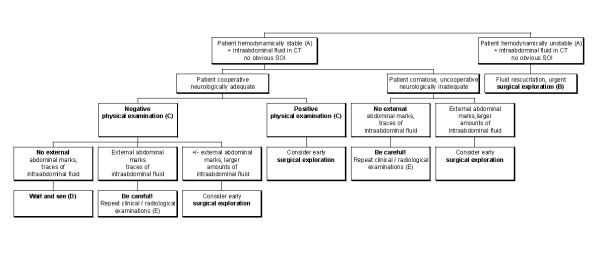
Figure 1.
The algorithm summarizes a possible plan of action for patients who have sustained blunt abdominal injury with suspected intraabdominal injury other than solid organ damage. (A) Patient can be stabilized with adequate fluid management. (B) Depending on local skill and availability of theatre resources, laparoscopy is the preferred method of choice. (C) Positive/negative physical examination: refers to clinical signs of peritonitis. (D) Small amounts of abdominal fluid, especially in the female patient, may be physiological. Even in the absence of any clinical signs and abdominal marks, the patient should be evaluated on a regular basis, as some injuries require a certain time to become clinically manifest. (E) The risk of intraabdominal injury is greatly increased if abdominal marks (such as seat belt marks) are present. Special care needs to be taken so as not to miss any changes in patient presentation.