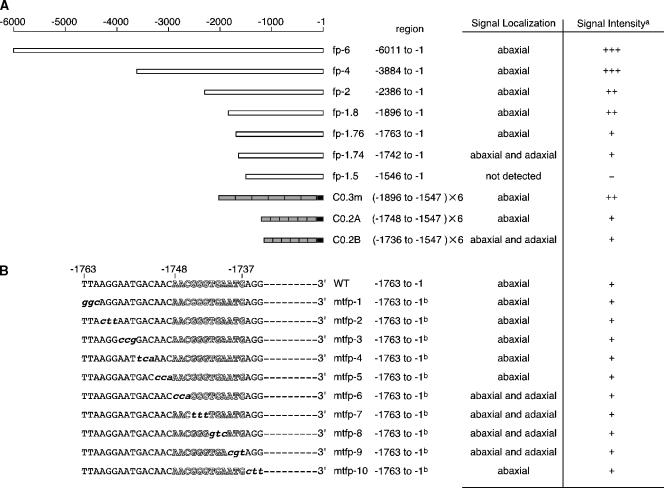
Figure 2.
Functional Analysis of the 5′ Regulatory Region of FIL.
GFP signal localization and intensity were examined with 20 independent transgenic plants for each construct.
(A) A series of deletions in the 5′ regulatory region of the FIL gene. White boxes indicate the 5′ regulatory region connected to the GFP coding region and the 3′ terminus of nopaline synthase. Gray boxes in C0.3m, C0.2A, and C0.2B have six tandem repeats of regions at −1896 to −1547, −1748 to −1547, and −1736 to −1547, respectively, connected to the minimal promoter from −46 to −1 in the 35S promoter of Cauliflower mosaic virus (black boxes) (Benfey et al., 1989; Benfey and Chua, 1990).
(B) A series of base substitutions in the region from −1763 to −1734. The 5′ regulatory region from −1763 to −1 with or without the substitutions was connected to the GFP coding sequence and the 3′ terminus of nopaline synthase. A predicted putative Kr binding site exists in the region from −1763 to −1734 (white letters).
a Relative levels of GFP expression are denoted as follows: +++, strong; ++, medium; +, weak; −, not detected. b A point-mutated sequence exists in the region from −1763 to −1734, but the other sequence is identical to that of the wild type.