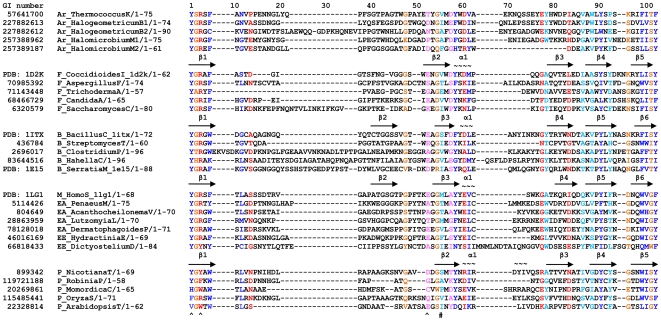
Figure 2. Structure-based multiple sequence alignment of the CID.
Hydrophobic positions with high conservation (C(i)≥0.45) are coloured in blue and positions with moderate conservation (0.35≤C(i)<0.45) are coloured in light blue. Hydrophilic positions with high conservation are coloured in red and positions with moderate conservation are coloured in pink. Neutral positions with high conservation containing mostly glycine, alanine, or proline are coloured in brown, while positions with moderate conservation are not highlighted. ‘∼’ and ‘→’ indicate the sequences in α-helices and β-strands, respectively. The secondary structure of tobacco chitinase CID was predicted by the program of PSIPRED. ‘ ^’ and ‘#’ represent the positions which form hydrogen bonding and the hydrophobic interaction with the substrate, respectively. Smaller alignments can be found in the following references: [24], [31], [33], [78]. The sequences from the following species are listed in the alignment: T. kodakarensis KOD1, Halogeometricum borinquense DSM 11551, Halomicrobium mukohataei DSM 12286, C. Immitis, A. fumigatus, Trichoderma atroviride, C. albicans SC5314, S. cerevisiae, B. circulans, Streptomyces thermoviolaceus, Clostridium paraputrificum, Hahella chejuensis KCTC 2396, S. marcescens, Homo sapiens, Penaeus monodon, Acanthocheilonema viteae, Lutzomyia longipalpis, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Hydractinia echinata, Dictyostelium discoideum AX4, Nicotiana tabacum, Robinia pseudoacacia, Momordica charantia, Oryza sativa, and Arabidopsis thaliana. The full genus name and the first letter of species name are shown for each organism in the figure. If two sequences are from one species, a number is added after the species name. All the sequences were obtained from the protein database at the NCBI. Abbreviations: Ar, Archaea; B, Bacteria; F, Fungi; P, Plantae; EE, early eukaryotes; EA, early Animalia; M, mammal.