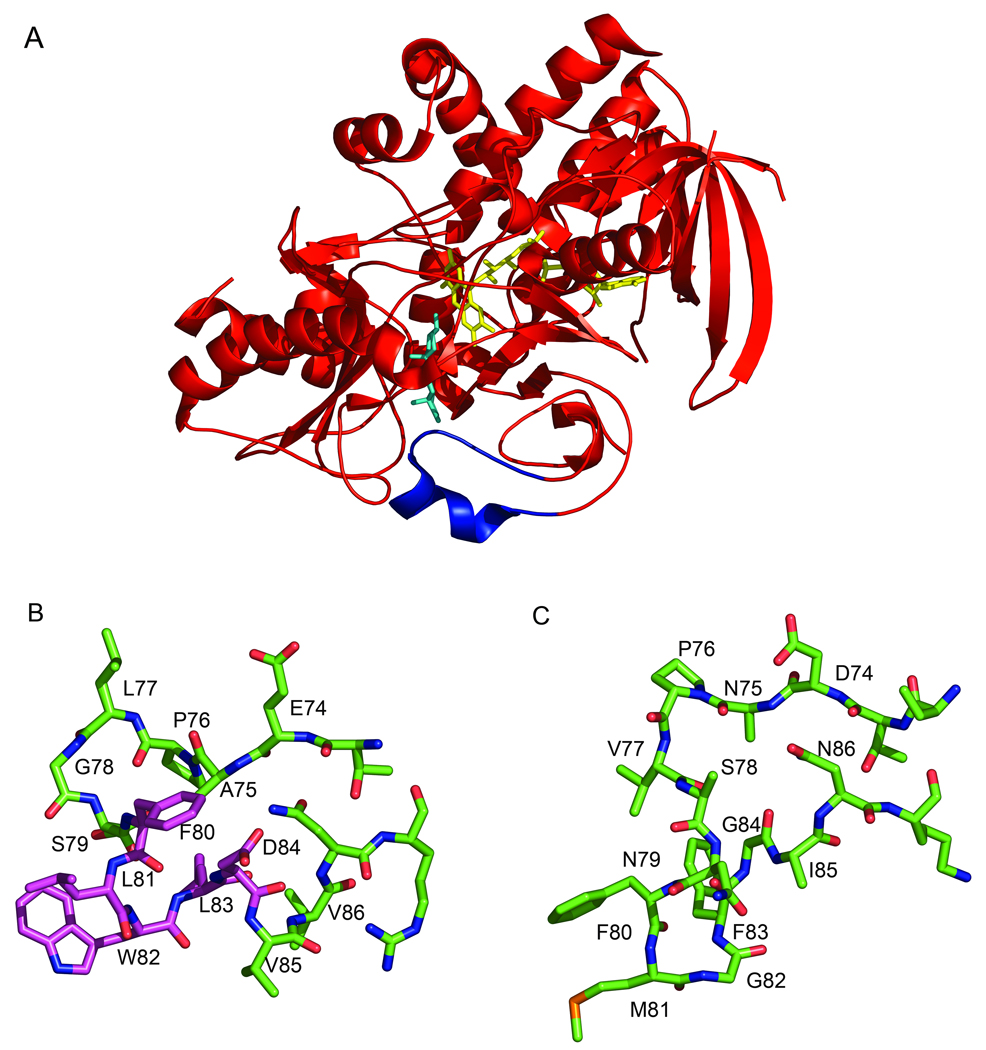
Fig. 1.
Three-dimensional structure of ChOx illuminating the active site loop. (a) Ribbon cartoon of Streptomyces ChOx (1MXT [3]) with epiandrosterone modeled into the active site (cyan). The FAD cofactor is shown in yellow. The active site loop that must move to allow substrate binding is shown in blue. (b) Stick atomic representation of Streptomyces ChOx active site loop from (a) in the same orientation. (c) Stick atomic representation of active site loop from Rhodococcus equi (formerly B. sterolicum) ChOx (1COY) [2]. The entire Rhodococcous ChOx structure was overlaid with the Streptomyces ChOx structure and the loops in (b) and (c) are depicted in the same enzyme orientations. Side-chains for which there is no electron density were modeled as alanines. The residues that were deleted in [32] are shown with a magenta carbon backbone. This figure was made with Pymol [103].