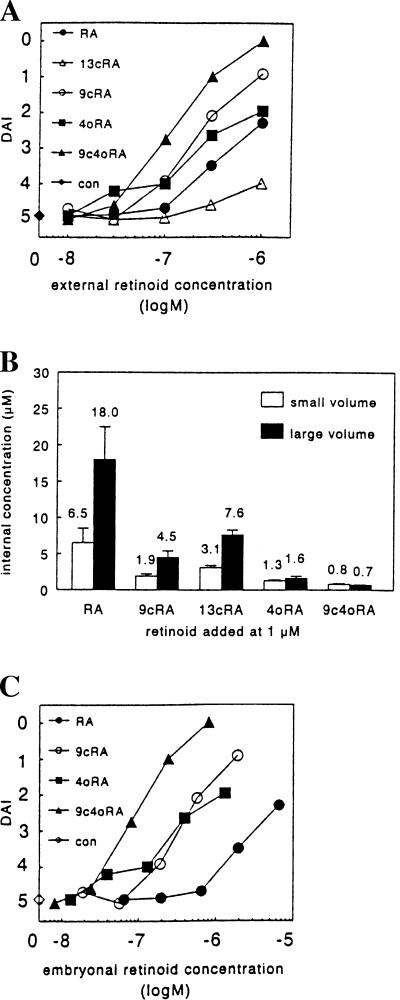
Figure 4.
9-Cis-4-oxo-RA (9c4oRA) disrupts Xenopus axis formation. (A) Dose–response curves for indicated retinoids, with external retinoid concentrations plotted on the x axis, and dorso-anterior index (see Fig. 3B) on the y axis. Embryos treated at 10 embryos/1 ml retinoid containing tap water from stage 10 (early gastrula) onwards. Data are means of 10 embryos. SD < 10%. con, control. (B) Uptake of medium applied retinoids by Xenopus embryos. Embryos bathed at 10 embryos/1 ml 10−6 M retinoid containing tap water (small volume) or 10 embryos/5 ml 10−6 M retinoid containing tap water (large volume) from stage 10–12 (5 hr at 20°C). Embryonal retinoid concentrations then were determined by HPLC. Data are means (above each bar in μM) ± SD. (C) Dose–response curves for indicated retinoids, using embryonal retinoid concentrations. Calculated from A, using correction factors for retinoid uptake derived from B: RA, 6.5; 9-cis-RA (9cRA), 1.9; 4-oxo-RA (4oRA), 1.3; 9-cis-4-oxo-RA (9c4oRA), 0.8. It is assumed that these correction factors, measured at 10−6 M external retinoid concentrations, are also valid for lower external retinoid concentrations. con, control.