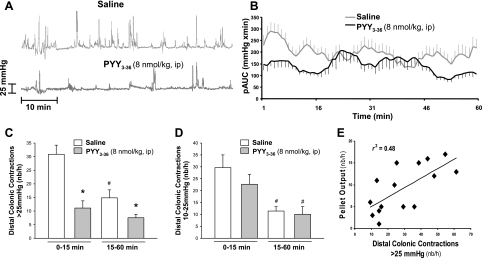
Fig. 4.
Intraperitoneal PYY3–36 reduces distal colonic intraluminal pressure using a noninvasive miniature pressure transducer inserted into the distal colon in restrained conscious mice. After intraperitoneal injection of PYY3–36 (8 nmol/kg, n = 9) or saline (n = 6), mice were briefly anesthetized for insertion of the pressure transducer, and distal intracolonic pressure was recorded 10 min later for 1 h. A: representative raw trace during the 1-h recording in mice injected with intraperitoneal saline and PYY3–36. B: time course of the phasic component of intraluminal pressure trace of area under curve (pAUC; mmHg × min) over 1-h recording. C: mean of distal colonic contractions (number/h) with high amplitude (>25 mmHg) in the first 15 min and in 15–60 min. D: mean of distal colonic contractions (number/h) with low amplitude (10–25 mmHg) in the first 15 min and in 15–60 min. F: correlation between 1-h distal colonic contractions (number/h) with high amplitude (>25 mmHg) and FPO. Data are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 vs. saline; #P < 0.05 vs. 0–15 min of the same treatement.