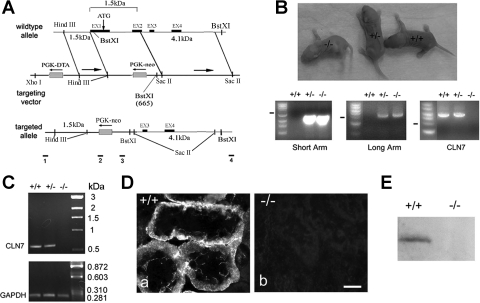
Fig. 1.
Generation of claudin-7 knockout mice. A: targeted-gene deletion strategy. Claudin-7 gene contains four exons as shown in wild-type allele. A replacement targeting vector containing a PGK-neo cassette was designed to delete exon 1, intron 1, and exon 2 of claudin-7 gene. Bars 1 and 2 underneath the targeted allele indicate the position of PCR primers for 5′ sequence (2.5 kb). Bars 3 and 4 indicate the position of PCR primers for the 3′ sequence (4.2 kb). B: production of claudin-7 knockout mice and their genotyping by PCR. Top: Cln7−/−, Cln7+/−, and Cln7+/+ mice at 3 days old. Bottom: genomic DNA was isolated from newborn mouse tail for genotyping analysis. The PCR products from both heterozygous (+/−) and homozygous (−/−) mice yielded a 2.5-kb band (short arm) and a 4.2-kb band (long arm) respectively, whereas the wild type (+/+) did not have these two bands. Wild-type and heterozygous mice produced a 5.7-kb band indicating the presence of claudin-7 gene (CLN7). This 5.7-kb band was absent in the homozygous mouse. C: verification of claudin-7 gene deletion in Cln7−/− mice by RT-PCR. The PCR products were expected as 634 bp for claudin-7 and 284 bp for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (serve as a PCR positive control). Claudin-7 mRNA was present in wild-type and heterozygous mice, but was absent in knockout mouse. D: loss of claudin-7 immunoreactivity in Cln7−/− mice. Kidneys from 1-wk-old Cln7+/+ (a) and Cln7−/− (b) mice were dissected and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Frozen sections (5 μm) of kidneys were immunostained with anti-claudin-7 antibody and detected by Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody. The images were taken at the kidney cortex region. Scale bar: 15 μm. E: Western blot analysis showed the presence of claudin-7 protein expression in Cln7+/+ but not in Cln7−/− mice. The membrane was probed with anti-claudin-7 antibody.