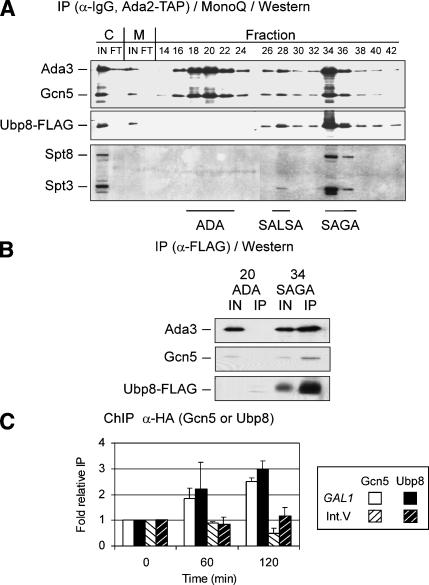
Figure 2.
Analysis of Ubp8 association within Ada2-containing complexes. (A) Chromatographic fractionation of Ubp8 from whole-cell extracts. Cell extracts containing Ada2-TAP and Ubp8-Flag were fractionated first via the TAP purification method (Puig et al. 2001) followed by MonoQ ion exchange chromatography. Even-numbered fractions (14-42) from the MonoQ column were subjected to Western blotting to detect Ubp8-Flag, which was compared with ADA/SALSA/SAGA-associated (as indicated) Ada3 and Gcn5, SALSA/SAGA-associated Spt3, and SAGA-specific Spt8. Samples from inputs (IN) and flowthroughs (FT) for calmodulin-bead binding (C) and MonoQ column (M) purification steps were included. (B) Association of Ubp8 in ADA or SAGA complexes. ADA and SAGA fractions eluted from the MonoQ column were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag affinity resin (Sigma), and subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect Ubp8-Flag, Ada3, and Gcn5. Input represents 30% of material in the immunoprecipitation. (C) ChIP analysis of Gcn5 and Ubp8 at the GAL1 promoter. Gcn5-3HA (open bars) and Ubp8-3HA (closed bars) binding in a wild-type background were analyzed by ChIP at the GAL1 promoter in glucose (0 time point) and in galactose (60 and 120 min time points). This association was compared with the Int. V region [Gcn5-3HA sample (open bars, black stripes) or Ubp8-3HA (closed bars, white stripes)]. Data are presented as fold relative IP with glucose input-normalized immunoprecipitated values set to 1.0 and all others compared with these samples.