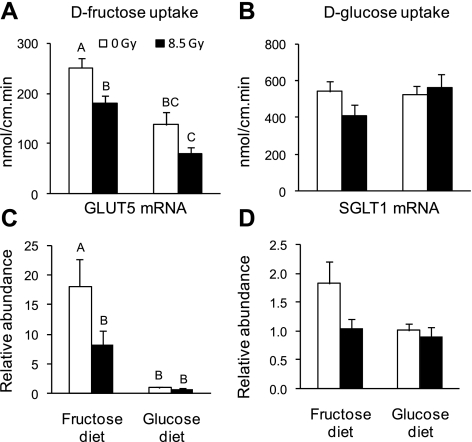
Fig. 7.
Effect of irradiation on rates of intestinal sugar uptake and on relative mRNA abundance of the sugars transporters of mice fed with high-sugar diets (experimental design in Fig. 1B). d-Fructose uptake (A) and d-glucose uptake (B) per centimeter at 8 days postirradiation at the proximal part of the small intestine of mice acutely gamma-irradiated at 0 Gy and 8.5 Gy. Mice were fed with 60% d-fructose or 60% d-glucose diet for 24 h (start specific diet at 7 days postirradiation), then killed. Relative (to d-glucose diet at 0 Gy) mRNA abundance of GLUT5 (C) and SGLT1 (D) is shown. Results are means ± SE (n = 6). Bars with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05). See text for P values. d-Fructose uptake rate and GLUT5 mRNA abundance increase in both irradiated and unirradiated mice fed a d-fructose diet. d-Fructose uptake rate and GLUT5 mRNA abundance decreased markedly in irradiated mice fed d-fructose.