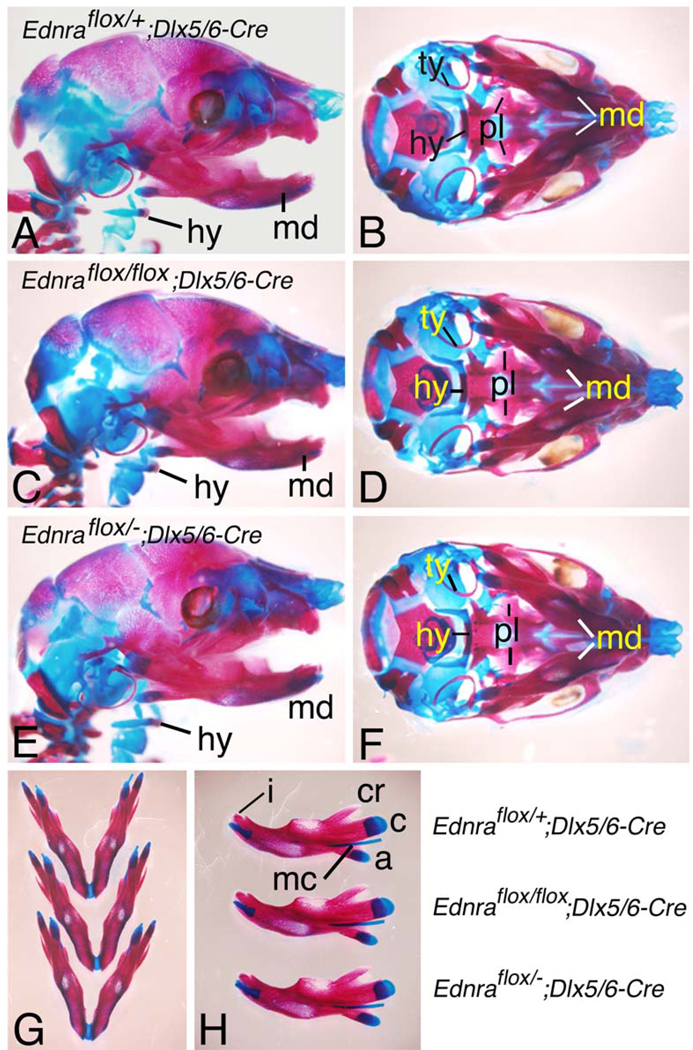
Fig. 2.
Analysis of jaw development in E18.5 Ednraflox/flox; Dlx5/6-Cre and Ednraflox/−; Dlx5/6-Cre conditional knockout embryos. Lateral (a,c,e), ventral (b,d,f,g) and intralateral (h) views of Ednraflox/+; Dlx5/6-Cre (control; a,b), Ednraflox/flox; Dlx5/6-Cre (c,d) and Ednraflox/−; Dlx5/6-Cre (e,f) conditional knockout embryos stained with alizarin red and alcian blue. a,f Regardless of the genotype, defects are not observed in any skeletal structures, including the mandible, Meckel’s cartilage, malleus and incisors. g,h In comparison to a control mandible, Ednraflox/flox; Dlx5/6-Cre and Ednraflox/−; Dlx5/6-Cre conditional knockout mandibles do not display any morphological differences in their shape, length or processes. a Articular process; c condylar process; cr coronoid process; i incisor; md mandible; mc Meckel’s cartilage; hy hyoid; ty tympanic ring