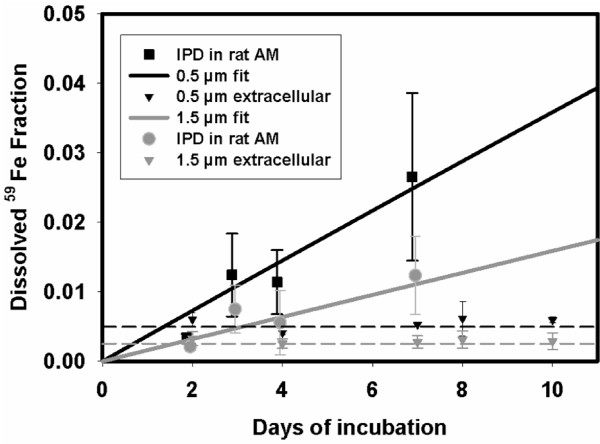
Figure 1.
Intracellular and extracellular dissolution of 1.5 and 0.5 μm 59Fe2O3 particles in alveolar macrophages (in vitro study). Rat alveolar macrophages (AM) or incubation media without AM were incubated in vitro with 59Fe-labeled 0.5 μm Fe2O3 particles and 1.5 μm Fe2O3 particles, respectively. The intracellular particle dissolution (IPD) rate for cells of 4 different animals (n = 4) and the extracellular dissolution for 4 different incubations without cells (n = 4) were determined over a period of 7 days. The small 0.5 μm particles exhibited a higher IPD rate (0.0037 ± 0.0014 d-1; n = 4) than the large 1.5 μm particles (0.0016 ± 0.0012 d-1; n = 4); both rates were corrected for extracellular particle dissolution see equation 3. The extracellular dissolution rate for both types of particles was negligible small.