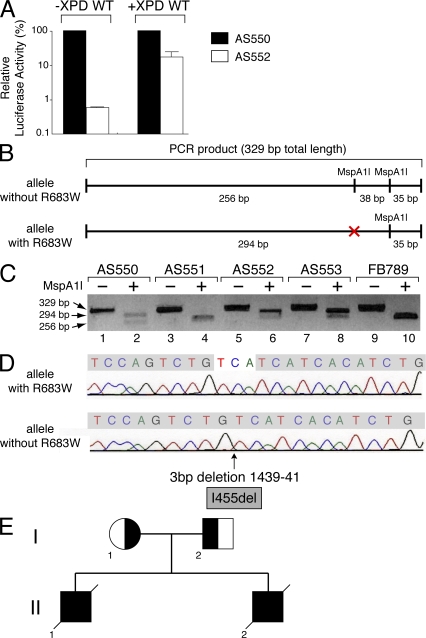
Figure 2.
Identification of the XPD mutations in the AS550 and AS552 patients. (A) Host cell reactivation in AS550 (filled columns) and AS552 (open columns). Fibroblasts were transfected with the pCMV-luc (500 ng) previously exposed to 1,000 J/cm2 of UVC-light (254 nm), pCH110 (100 ng, encoding the β-galactosidase which was used to normalize transfection efficiencies), and either empty pcDNA (10 ng; left pair of columns) or pcDNA XPD WT (10 ng, XPD WT; right pair of columns). Host cell reactivation was measured as the relative luciferase activity caused by the repair of the UV-damaged luciferase gene. The values of three independent experiments are presented as percentages, 100% being the level of luciferase activity obtained in AS550 cells. (B) Scheme representing the PCR products obtained from XPD allele with or without the point mutation R683W, which corresponds to a C-to-T substitution at the first base of exon 22 in the gene. This mutation abolishes the restriction site for the endonuclease MspA1l. (C) PCR products were obtained from genomic DNA of AS550, AS551, AS552, AS553, and FB789 (used as control) fibroblasts. Restriction fragment length polymorphism assay was performed from the PCR products digested by MspA1l. (D) DNA sequencing of the PCR product obtained from cDNA of AS552 cells. The XPD allele without the R683W point mutation has a deletion of three bases (TCA) at position 1439–41, giving rise to an amino acid del455 in-frame (I455del). (E) Genetic pedigree of the family of the patients AS552 and AS553. The mother AS550 (I-1) carries the XPD mutation that corresponds to an amino acid substitution at position R683W. The father AS551 (I-2) carries a deletion of three bases (TCA) at position 1439–41 that makes amino acid del455 in-frame (I455del). The deceased patients AS552 (II-1) and his brother AS553 (II-2) had compound heterozygous mutations that corresponded to the substitution at R683W (maternal) and the deletion I455del (paternal), resulting in the development of XP with skin cancer and neurological degeneration.