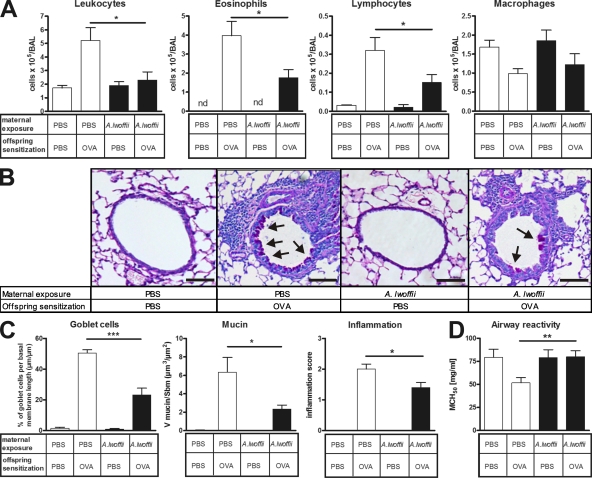
Figure 1.
Prenatal A. lwoffii F78 exposure significantly prevented the extent of the asthmatic phenotype in the offspring. White bars represent offspring exposed prenatally to control PBS, and black bars represent offspring exposed prenatally to A. lwoffii F78. (A) Differential leukocyte numbers in the BAL of offspring. (B) Representative lung tissue cross sections stained with PAS to visualize mucus-producing goblet cells (arrows) and airway inflammation in offspring. Bars, 100 µm. (C) Quantification of mucus-producing goblet cells, mucus volume, and inflammation in offspring airways. (D) Offspring airway responsiveness to MCh. Results represent one out of two independently performed experiments with similar outcomes (n ≥ 8 per group). Means ± SEM are shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.