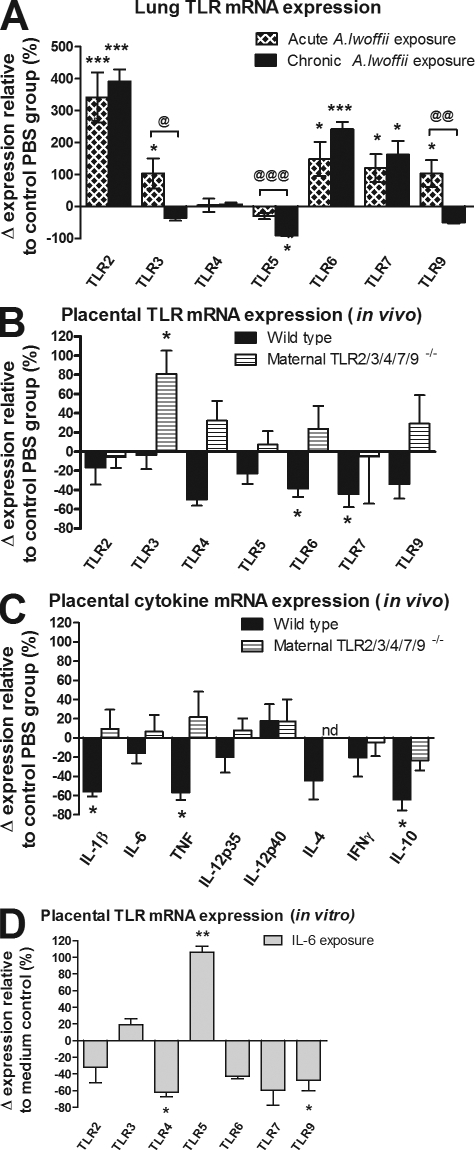
Figure 4.
Maternal treatment with A. lwoffii F78 modulates expression of immune-relevant genes in lung and placental tissue. Bars represent the relative change in mRNA expression in the treated compared with the control group. All mRNA expression levels were calculated by setting the mRNA expression of the control group as 100% and individually calculating the Δ expression for each mRNA sample. The calculated change in mRNA expression for each noncontrol individual was then plotted, and the mean and SEM calculated. (A) TLR mRNA expression in the wild-type maternal lung 4 h after intranasal A. lwoffii F78 exposure for both a single acute exposure and a 5-wk chronic exposure. (B) TLR mRNA expression in placentas from both wild-type and TLR2/3/4/7/9−/− mice on day 18 of gestation. (C) Cytokine mRNA expression in placentas from both wild-type and TLR2/3/4/7/9−/− mice on day 18 of gestation. (D) TLR mRNA expression from wild-type primary placental cell culture incubated with IL-6. In vivo results are from two independently performed experiments with similar outcomes (n ≥ 5 animals per group with two placentas per animal). In vitro results are from one experiment performed in triplicate (n = 3 per group). Means ± SEM are shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 for the treated group compared with control. @, P < 0.05; @@, P < 0.01; and @@@, P < 0.001 for acute versus chronic treatment. nd, not detectable.