Fig. 1.
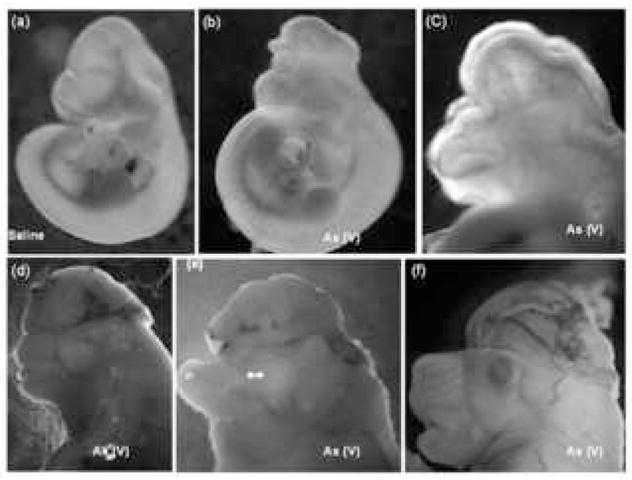
Predominant phenotypes resulting from in utero arsenic exposure of pregnant mice. Dams were dosed i.p. with 20 mg/kg of pentavalent sodium arsenate on gestation days (gd) 7 and 8, euthanized on gd 10 or 17, and embryos/fetuses removed for observation and photography. Prominent phenotypes generated include isolated exencephaly (b [gd10] and f [gd18]), complete cranial/facial clefting (c [gd10]), exencephaly and midfacial hypoplasia (d [gd17]), acrania (e [gd17]), and gastroschisis (not shown). Panel (a) shows a saline control embryo on gd 10.
