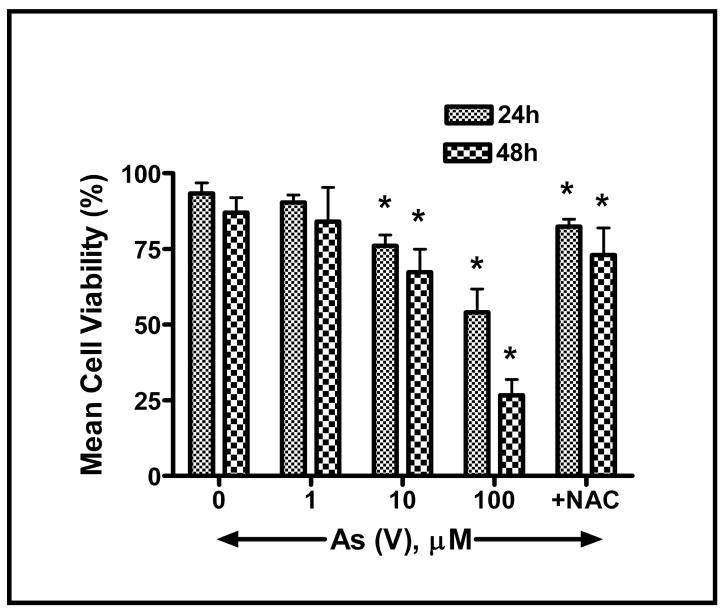
Fig. 4.
Assessment of cell viability subsequent to arsenate-induced apoptosis in MEMM cells. Trypan blue dye exclusion was used to assess viability of harvested MEMM cells 24 or 48 h after treatment with different concentrations of As (V). Viable cells retain their membrane integrity and thus exclude the dye. Non-viable cells appeared blue and were quantified using a hemocytometer. The percentage of viable cells was plotted against arsenate concentration. Cells pretreated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) are protected from As (V)-induced apoptosis. Nearly 70% of MEMM cells remained viable after 48 h of treatment with 100 μM As (V), compared to 12–15% of similarly treated cells that did not receive NAC pretreatment. In each case, mean values ± S.E. from three separate experiments with similar results were plotted. *p<0.05.