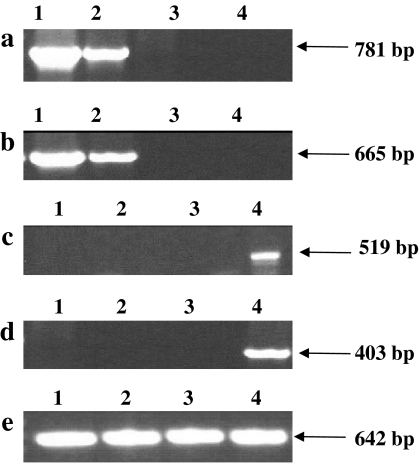
Fig. 5.
PCR and RT-PCR analysis of wild type, tla1 and two tla1-complemented strains. Lane 1 tla1-comp1, lane 2 tla1-comp2, lane 3 tla1 mutant, lane 4 wild type. a Genomic DNA PCR product of 781 bp was obtained with forward PsaD 5′ UTR “primer 5” and reverse TLA1 Exon-2 “primer 4” (Fig. 1S and Table 1S; supplementary material). No products were obtained with the tla1 mutant (lane 3) or wild type samples (lane 4). b RT-PCR products of 665 bp were obtained with forward PsaD 5′ UTR “primer 5” and reverse (TLA1 Exon-2 “primer 4” (Fig. 1S and Table 1S; supplementary material) from the cDNA of the tla1-complements (lanes 1 and 2). No products were obtained from the cDNA of the tla1 mutant (lane 3) or wild type samples (lane 4). c Genomic DNA PCR product of 519 bp was obtained with forward TLA1 5′ UTR “primer 1” and reverse Exon-2 “primer 3” from the wild type sample only (lane 4). d RT-PCR product of 403 bp was obtained with forward TLA1 5′ UTR “primer 1” and reverse Exon-2 “primer 3” with the wild type cDNA only lane 4). e RT-PCR products of 642 bp were obtained with all samples when using forward Exon-1 “primer 2” and reverse Exon-2 “primer 4”. Genomic DNA and RNA for PCR and RT-PCR were extracted from cells grown photosynthetically in minimal TBP liquid media