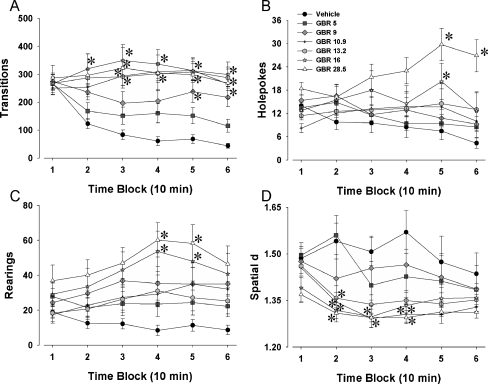
Fig. 3.
Effects of GBR 12909 on exploratory behavior in 129/SvJ mice in the mouse BPM. Mice (129/SvJ) were administered various doses (5, 9, 10.9, 13.2, 16, and 28.5 mg/kg) of the selective DAT inhibitor GBR 12909 immediately prior to the assessment of their exploration in the mouse BPM. Exploration was measured in the BPM for activity levels—transitions (a), exploration—holepoking (b) and rearing (c), as well as locomotor patterns—spatial d (d). GBR 12909 increased activity at various doses tested, only 16 and 28.5 mg/kg initially but also 9, 10.9, and 13.2 mg/kg by the end of testing (a). The effects of GBR 12909 on exploration were similar for the two measures, with 16 and 28.5 mg/kg increasing holepoking (b) and rearing (c) toward the end of the test session. Doses of GBR 12909 larger than 10.9 mg/kg also lowered spatial d, although this effect was seen predominantly between 10 and 40 min (d). Data presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 when compared to vehicle administered control mice. Scales on the x-axes differ from Figs. 1 and 2 due to differing basal activity levels of C57BL/6J and 129/SvJ mice