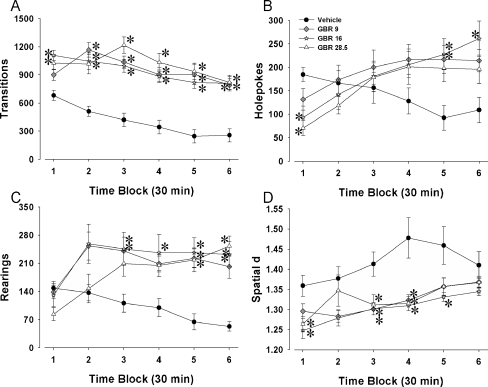
Fig. 4.
Time course of the effects of GBR 12909 on exploratory behavior in C57BL/6J mice in the mouse BPM. Mice were administered the selective DAT inhibitor GBR 12909 at various doses (9, 16, and 28.5 mg/kg) immediately prior a 3-h assessment of their exploration in the mouse BPM. Activity levels—transitions (a), exploration—holepoking (b) and rearing (c), as well as locomotor patterns—spatial d (d) were all measured. GBR 12909 increased activity at various doses tested, only 16 and 28.5 mg/kg initially but also 9 mg/kg throughout the 3-h period (a). Despite an initial drop in holepoking, GBR 12909 at 16 mg/kg consistently increased holepoking (b) and rearing (c). GBR 12909 at 16 mg/kg also consistently lowered spatial d (d), with some modest effects at 9 and 28.5 mg/kg as well. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 when compared to vehicle administered control mice