Figure 3.
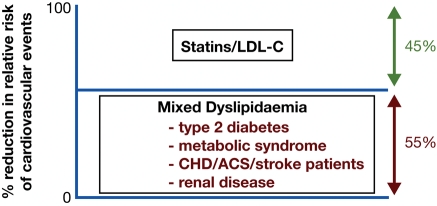
Cardiovascular risk remains high despite aggressive statin therapy. Statin treatment across a wide range of lipid phenotypes in patients at high cardiovascular risk has been highly successful in reducing relative risk by up to 45%. Nonetheless, major residual cardiovascular risk remains, part of which is due to non-modifiable risk factors but equally to modifiable risk factors. Atherogenic mixed dyslipidaemia is a frequent component of the latter, thereby suggesting that therapeutic attenuation of risk in this phenotype, which involves elevated levels of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and small dense low-density lipoprotein, with subnormal levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apoA-I, would contribute to further reduction in residual risk across a wide range of metabolic disease states. ACS, acute coronary syndrome; CHD, coronary heart disease; LDL-C, LDL cholesterol.