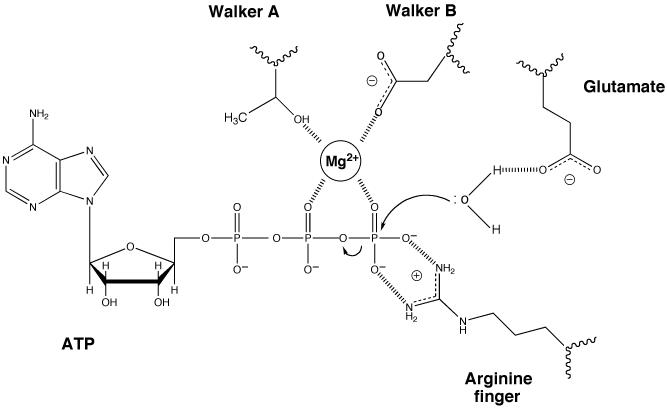
Figure 1. Essential residues in the active site of ATPases.
ATP hydrolysis is promoted by several residues in this generalised active site of ATPases. Only residues with an established role in catalysis rather than binding are shown. When present, the “arginine finger” is usually provided in trans from an adjacent subunit or domain. The magnesium ion can be coordinated in different ways but that shown is one of the most common involving interactions with a threonine (or serine) from the Walker A motif, an aspartate from the Walker B motif and oxygens from the β and γ phosphates of the ATP. The role of the glutamate residue (in the DExx motif of AAA+ proteins) is to activate a water molecule by making the oxygen more electronegative and hence a better nucleophile for attack of the γ-phosphorus.