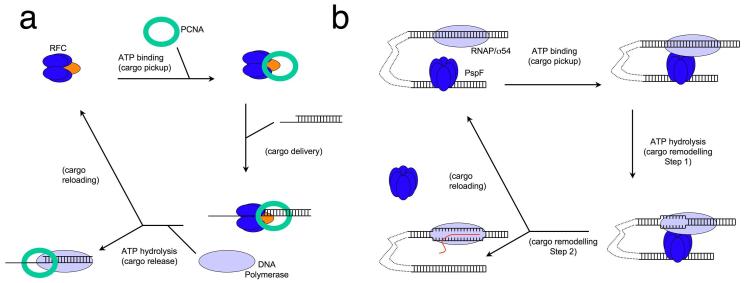
Figure 5. Overall mechanism of two well characterised AAA+ protein catalysed reactions.
(a) PCNA clamp loading by Replication Factor C. Upon ATP binding, RFC forms a stable complex with PCNA (cargo pickup) that is competent to load onto DNA at primer-template junctions (cargo delivery). ATP hydrolyis by the small subunits (blue) releases PCNA (cargo release) which is then bound by DNA polymerase. Finally, ATP hydrolysis at the large subunit (orange) recycles the RFC and allows pick up of the next PCNA (cargo reloading).
(b) Bacterial transcription activation by PspF. Upon ATP binding, PspF, which binds to the DNA sequence upstream of transcription start site, interacts with RNAP/σ54 through DNA looping (cargo pickup). At the point of ATP hydrolysis, PspF forms a stable complex with RNAP/σ54 and initial remodelling of RNAP/σ54/DNA occurs (cargo remodelling). Upon the completion of ATP hydrolysis, transcription proceeds and PspF dissociates from the complex (cargo remodelling and reloading).