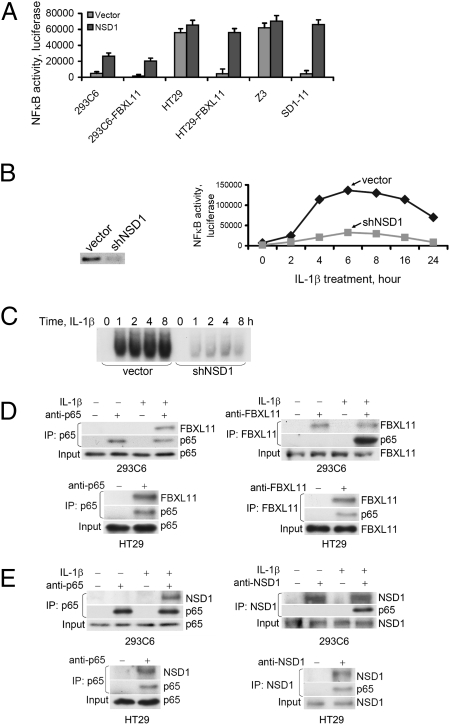
Fig. 1.
NSD1 activates NF-κB and reverses the inhibitory effect of FBXL11; FBXL11 and NSD1 bind to p65 upon NF-κB activation. (A) Luciferase assay of NF-κB activity. Expression of NSD1 activates NF-κB and reverses inhibition caused by increased expression of FBXL11 in different cells, including 293C6, HT29, and mutant Z3 cells, and corresponding cells in which FBXL11 is overexpressed. Results of triplicate luciferase assays are shown as means ± SD. (B) (Left) Western assay showing knockdown of expression of NSD1 in 293C6 cells with shRNA. (Right) Luciferase assay of NF-κB activity in 293C6 cells treated with IL-1β for different times, showing that reduced expression of NSD1 by shRNA decreased NF-κB activity. Results of triplicate luciferase assays are shown as means ± SD. (C) EMSA assay of NF-κB in 293C6 cells treated with IL-1β for different times, showing that reduced NSD1 expression by shRNA decreased NF-κB DNA binding activity. (D and E) p65 Coimmunoprecipitates with FBXL11 and NSD1; FBXL11 and NSD1 bind to p65 only when NF-κB is activated. Immunoprecipitation (IP) assays detect binding of endogenous FBXL11 or NSD1 to p65, either in 293C6 cells treated with IL-1β (Upper) or in HT29 cells with constitutive NF-κB activation (Lower).