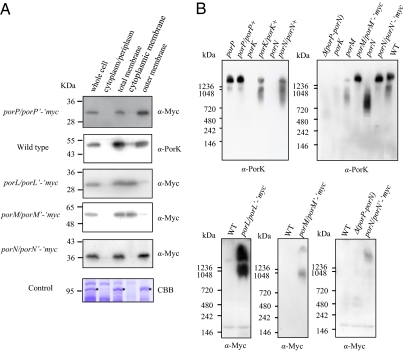
Fig. 2.
Subcellular location of PorP, PorK, PorL, PorM, and PorN proteins and formation of a large complex. (A) Subcellular location of the Por proteins. The cell lysates of P. gingivalis strains were subjected to detergent fractionation followed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti-PorK antibody for the wild-type strain, and anti-Myc antibody for the porP/porP’-‘myc, porL/porL’-‘myc, porM/porM’-‘myc, and porN/porN’-‘myc strains. As a control, a major outer membrane protein, RagA, which was identified by mass spectrometry, is indicated by an asterisk (*). CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. (B) Detection of protein complexes by Blue Native PAGE. Cell lysates of P. gingivalis strains were subjected to 3–12% gradient Blue Native PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti-Myc antibody and anti-PorK antibody.