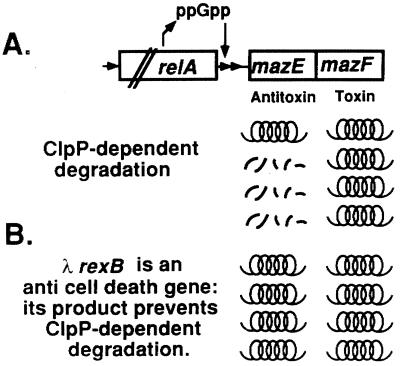
Figure 4.
A model for the E. coli rel mazEF-mediated cell death (A) and the anti-death effect of λRexB (B). (A) Under conditions of nutritional starvation, the level of ppGpp increases. During amino acid starvation, this increase in the cellular level of ppGpp is achieved by the interaction of the product of relA with uncharged tRNA (33). ppGpp inhibits the coexpression of mazE and mazF. MazF is a long-lived toxic protein, whereas MazE is an antitoxic labile protein that is degraded by the ClpPA protease. Therefore, when the cellular level of ppGpp is increased, the concentration of MazE is decreased more rapidly than that of MazF, and thus MazF can exert is toxic effect and cause cell death (20). (B) λRexB antagonizes the ClpP family of proteases. As a result, it inhibits the degradation of the antitoxic protein MazE and thereby prevents cell death.