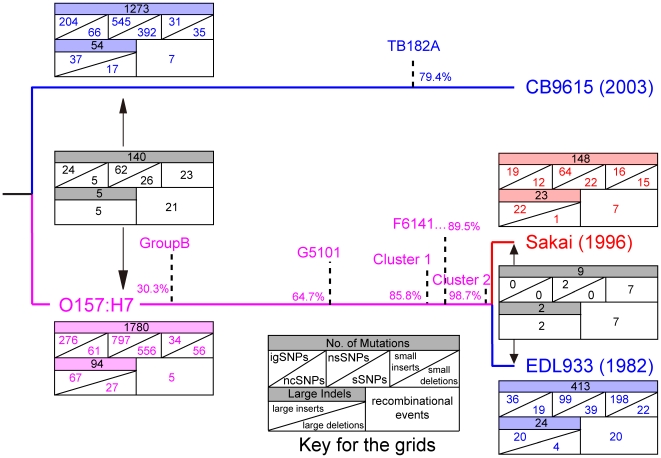
Figure 2. Tree showing the relationships of CB9615 and 2 O157:H7 strains.
The tree topography is taken from the alignment of 26 completed genomes (Figure 3) and Whittam [7]. For each lineage the number of mutations (including small indels), recombination events and insertion or deletion events (large indels) are shown in a grid, as specified with the key. Mutations are shown as intergenic, other non-coding, non-synonymous or synonymous SNPs (igSNPs, ncSNPs, nsSNP, sSNPs), small insertions and small deletions or indels if not differentiable. Large indels are separated into insertions or deletions where possible. Events allocated to the divergence between CB9615 and O157:H7, or between Sakai and EDL933, respectively, but not to either lineage, are shown in the grids between the two lineages. The branch point estimates for group B [12] including strain 493-89), G5101 and F6141, and clusters 1 (Strains 14359 and 87-14) and 2 (86-24) are marked with dotted lines on the O157:H7 lineage, and TB182A on the O55:H7 lineage. The distribution of SNPs along that lineage is based on reanalysis of data from Zhang et al. [17] and Leopold et al. [12].