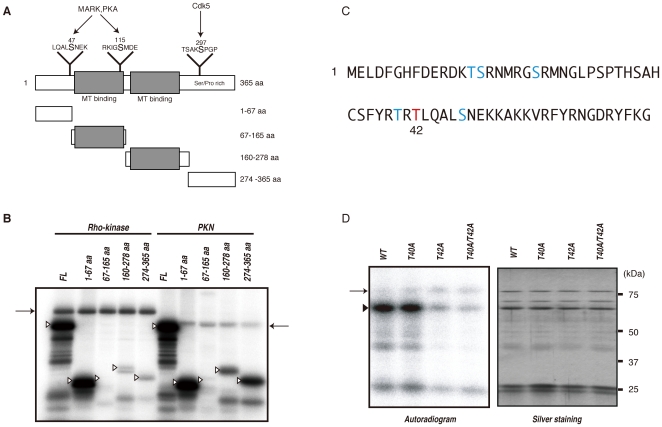
Figure 4. Identification of phosphorylation sites of DCX by Rho-kinase.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain structures and deletion mutants of DCX. Sites phosphorylated by MARK, PKA and Cdk5 are also shown. (B) Phosphorylation of DCX deletion mutants. The indicated GST-DCX fragments were phosphorylated by GST-Rho-kinase-cat or GST-PKN-cat. The phosphorylated proteins were imaged by autoradiography. Open arrowheads and arrows indicate the positions of substrates and autophosphorylation of kinases, respectively. These results are representatives of at least three independent experiments. (C) Sequence of and potential phosphorylation sites within the 1–67 aa region. The major phosphorylation site was identified as Thr42 (red). (D) Phosphorylation of DCX mutants with amino acid substitutions. GST-DCX-WT, -T40A, -T42A or -T40A/T42A was incubated with Rho-kinase-cat and 50 µM [γ-32P] ATP for 10 min at 30°C. The reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS-PAGE and GST-fused proteins were visualized by silver staining (right). Phosphorylated proteins were imaged by autoradiography (left). Arrowhead and arrow indicate the positions of substrates and autophosphorylation of kinase, respectively. These results are representatives of at least three independent experiments.