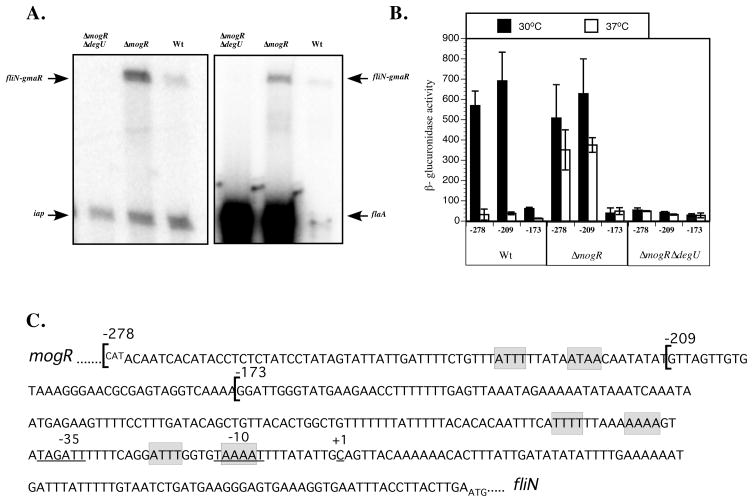
Figure 3. The fliN-gmaR promoter is DegU-activated.
A. Analysis of fliN-gmaR transcripts by primer extension. RNA was extracted from ΔmogRΔdegU, ΔmogR and wild-type (Wt) strains grown at 30°C in BHI broth for 6 h. Transcript specific primers were end-labeled with [γ32P]-ATP. Primer extension products were separated on a 5% denaturing acrylamide gel and detected by a phosphorimager. Primers for flaA and iap were included in independent experiments as controls.
B. Analysis of fliN-gmaR promoter activity as determined by β-glucuronidase assay. Transcriptional fusions of fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA to gusA were integrated in single copy into the tRNAArg locus of wild-type (Wt), ΔmogR, or ΔmogRΔdegU bacteria. Cultures were grown in BHI broth at 30°C or 37°C for 18–20 h prior to analysis. β-glucuronidase activities represent the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. Numbers correspond to fusions harboring −278, −209, or −173 through +274 relative to the transcriptional start of fliN-gmaR.
C. DNA sequence of the mogR-fliN intergenic region. The DNA sequence begins with the start codon (negative strand) for mogR and ends with the start codon for fliN. The transcriptional start site of the fliN-gmaR promoter (+1) was identified by primer extension and is underlined along with the predicted −35 and −10 elements. Transcriptional fusions of the fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA (−278, −209, −173 through +274 relative to the transcriptional start) are indicated by brackets and were fused to a gusA reporter and analyzed in Figure 2B. The predicted MogR binding sites are shaded in grey.