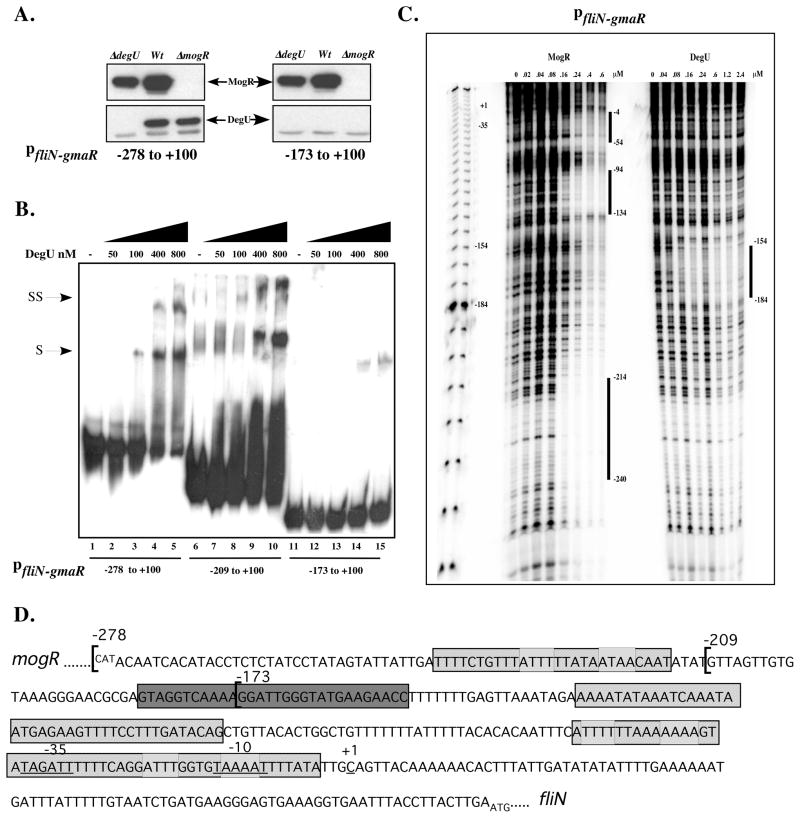
Figure 4. DegU binds directly to fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA.
A. Affinity purification of proteins that specifically bind fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA. Whole cell lysates of wild-type (Wt), ΔdegU, or ΔmogR bacteria were incubated at RT with magnetic Dynabeads coupled to fliN-gmaR specific promoter region fragments (−278 to +100 or −173 to +100 relative to the transcriptional start site). DNA-Bead complexes were washed, proteins were eluted and then separated by SDS-PAGE. DegU- or MogR- specific polyclonal antibody was used for Western blot detection. Arrows indicate DegU and MogR.
B. Gel shift analysis of DegU binding to fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA. Radiolabeled fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA fragments spanning −278, −209, or −173 to +100 relative to the transcriptional start site were incubated at RT with increasing amounts of purified His6-tagged LmDegU. Binding reactions were separated by non-denaturing PAGE and detected by autoradiography. Shifted (S) and Super-shifted (SS) complexes were detected.
C. DNase I footprint analysis of MogR and DegU binding to fliN-gmaR promoter region DNA. A radiolabeled DNA probe spanning the fliN-gmaR promoter region from −278 to +100 relative to the transcriptional start site was incubated at RT with increasing amounts of purified His6-tagged LmDegU or MogR and subsequently treated with DNaseI. Samples were run on a denaturing 6% acrylamide gel and the footprint was detected by phosphoimager. Binding sites are labeled with negative numbers relative to the transcriptional start site.
D. DNA sequence of the mogR-fliN intergenic region showing DegU and MogR binding sites. The DNA sequences corresponding to the three regions of MogR binding as identified in Figure 4C by DNaseI footprint analysis are shaded with cross-hatches. The predicted MogR binding sites are marked with light grey boxes. The DegU footprint as identified in Figure 4C is shaded with dark grey.