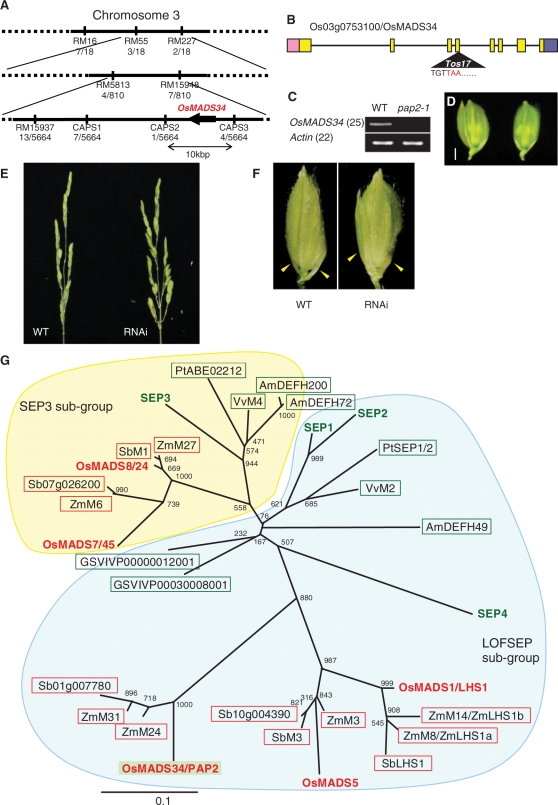
Fig. 3.
Isolation of PAP2 by positional cloning. (A) Location of the PAP2 locus on rice chromosome 3. The numbers of recombinants are indicated under each marker. (B) Structure of the PAP2/OsMADS34 gene. The boxes indicate exons, the line indicates introns and the triangle shows the insertion of Tos17. (C) Steady-state level of PAP2/OsMADS34 mRNA in the shoot apex of the wild-type and pap2-1. (D) Complementation test of pap2-1 by PAP2/OsMADS34. The elongated sterile lemma phenotype of pap2-1 (left) was rescued in the complemented plant (right). (E) Reduction of OsMADS34 mRNA accumulation phenocopied the pap2-1 phenotype. Panicles in an untransformed wild-type plant (left) and the OsMADS34 knock-down plant (right). (F) Spikelets in an untransformed wild-type plant (left) and the OsMADS34 knock-down plant (right). Yellow arrows show sterile lemmas. Sterile lemmas are elongated in spikelets of OsMADS34 knock-down plants, resembling those of the pap2-1 mutant. (G) Phylogenetic tree of SEP genes in plants. Amino acid sequences in the M-box and K-box were used for the analysis. The phylogenetic analysis was conducted using the Clustal W program, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by the Neighbor–Joining method. Bootstrap values from 1,000 replicates are indicated at each node. Letters in red indicate rice genes and letters in green indicate Arabidopsis genes. Genes shown in the red boxes are from grass species, whereas genes in the green boxes are from eudicots. Os, rice; Zm, maize; Vv or GSVIVP, grape; Pt, poplar; Sb, sorghum (Sorghum bicolor); At, Arabidopsis; Am, snapdragon.