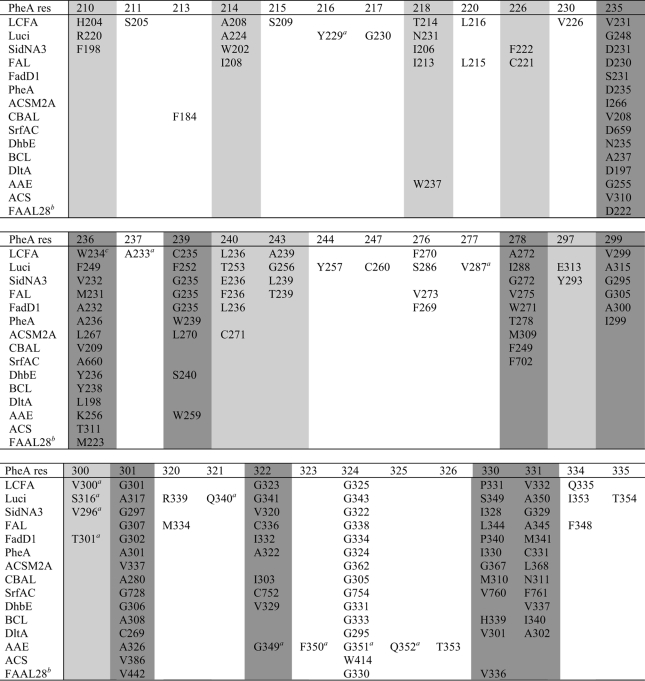
TABLE 4.
The pocket-lining residues in the acetyl-CoA synthetase-like superfamily
The dark gray shading denotes the PheA pocket-lining residues, and the light gray shading denotes the extra SidNA3 pocket-lining residues. The structures are as follows: long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (LCFA) (code 1v26), T. thermophilus long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (43); Luci (code 2d1s), Japanese firefly Luciola cruciata luciferase (47); SidNA3 (this work), N. lolii third adenylation domain from SidN; FAL (code 3gqw), E. coli fatty-acid-AMP ligase; FadD1 (code 3g7s), Archaeoglobus fulgidus long chain fatty-acid-CoA ligase; PheA (code 1amu), B. brevis adenylation domain from gramicidin S synthetase A (9); ACSM2A (code 3eq6), Homo sapiens medium chain acyl-CoA synthetase (50); CBAL (code 1t5d), Alcaligenes sp. AL3007 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA ligase (51); SrfAC (code 2vsq), B. subtilis adenylation domain from surfactin synthetase C (17); DhbE (code 1md9), B. subtilis DhbE adenylation domain (16); BCL (code 2v7b), Burkholderia xenovorans benzoate-CoA ligase (52); DltA (code 3dhv), Bacillus cereus d-alanyl-carrier protein ligase (53); AAE (code 3etc), Methanosarcina acetivorans acyl-CoA synthetase (54); ACS (code 1pg4), Salmonella enterica acetyl-CoA synthetase (7); and FAAL28 (code 3e53), Mycobacterium tuberculosis fatty acyl-AMP ligase 28 N-terminal domain (55). The American firefly Photinus pyralis luciferase (42, 56), B. subtilis d-alanyl-carrier protein ligase (6), and the Salmonella typhimurium (57) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (58) acetyl-CoA synthetases are not included in the table due to the high similarity of their binding sites to the homologous structures that are included.
a Only the main chain atoms of these residues line the pocket.
b The binding pocket exposed to solvent in the FAAL28 structure, which was solved in unliganded form, is too small to accommodate its long chain fatty acid substrate. There is an internal cavity in the protein closed off by Met-233. Met-233 is the equivalent of the Trp-234 residue in long chain fatty acid, which closes off the entrance to the binding pocket in the unliganded form and opens up upon ATP binding. Thus, it is likely that Met-233 in FAAL28 is performing a similar function and that the true binding pocket is much larger.
c In long chain fatty acid, sequence alignments place Asn-232 as the equivalent of the PheA residue 236, but structural comparisons show that it is actually Trp-234 that is the structurally equivalent residue due to an alternate main chain route.