Figure 1.
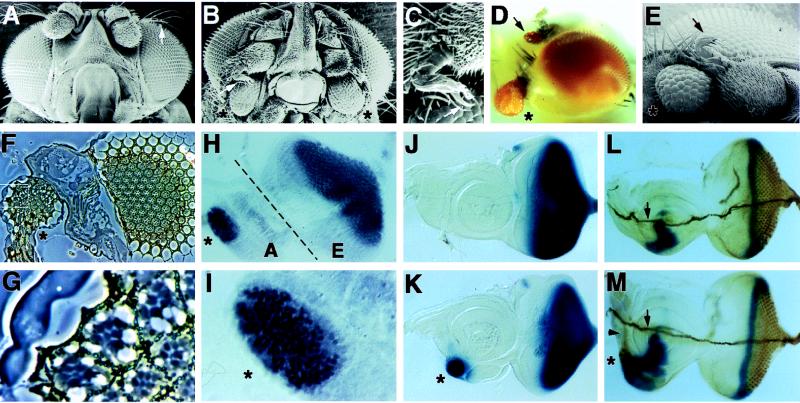
Targeted expression of tsh induces ectopic retinal development. (A and B) Scanning electron microscopy pictures of wild-type and Four eyes head morphology, respectively. Note the presence of two ectopic eyes (asterisks) in the Four eyes mutant. Also note that the arista (arrow in A), a thin branched structure on the antenna, was replaced with a leg-like structure in Four eyes (arrow in B; shown at higher magnification in C). Like normal legs, a claw (arrow in C) is present at the distal tip of this leg-like structure. (D) A light microscope image of a Four eyes fly. One ectopic eye is present at the anterior ventral surface of the head (asterisk), and another ectopic eye is present on a proximal segment of the antenna (arrow). (E) Scanning electron microscopy image of a transgenic fly expressing a full-length tsh cDNA in the pDMR vector. Note the presence of the ectopic eye (asterisk) and the arista-to-leg transformation (arrow). (F) A section through an ectopic eye (marked by an asterisk, to the left) and the normal eye (to the right) in a Four eyes mutant fly. A higher magnification of the outlined area in the ectopic eye is shown in G. Note the presence of cone cells, pigment granules, and rhabdomeres in the ectopic eye and that some ommatidia have normal numbers of photoreceptors. (H) A Four eyes eye (E)-antenna (A) disc stained with the Elav antibody. Note the presence of ectopic Elav staining in the antennal disc (asterisk), which normally does not express Elav. (I) A higher magnification of a portion of the antennal disc where ectopic Elav staining is observed. (J and K) glass expression in wild-type and Four eyes eye-antenna discs, respectively. Note the presence of ectopic glass expression (asterisk in K) in the antennal disc in Four eyes. Anterior is to the left and dorsal is up. (L and M) Wild-type and Four eyes eye-antenna discs, respectively, stained for dpp/lacZ (blue) and 22C10 (brown). Note that ectopic 22C10 staining can be seen both in the cell bodies of the ectopic photoreceptors (asterisk) and on their axon tracts (slightly out of focus, arrowhead in M). On a different focal plane (data not shown), we observed that the axons projected medially and then stopped; they did not fasciculate with the Bolwig’s nerve (arrows in L and M).