Figure 1.
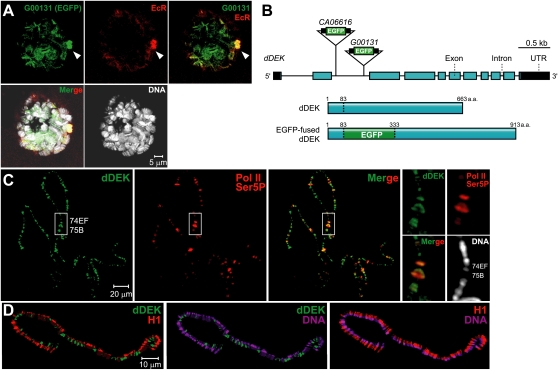
Localization of dDEK within the ecdysone-induced puff. (A) Third instar larval salivary gland nuclei of the G00131 protein trap line in which the EGFP-fused protein (green) colocalizes with the EcR (marked by an anti-EcR antibody, stained red) at ecdysone-induced puff loci (arrowhead) and interbands on polytene chromosomes (DNA stain, white). (B) Insertion sites of protein trap lines in G00131 and CA06616. (Top) The dDEK transcript fused to the EGFP exon (green box) carried by line G00131 or CA06616. The untranslated region (black), coding regions (blue), and insertion alleles (triangle) are shown. (Bottom) Schematic representation of deduced EGFP-fused dDEK proteins expressed in G00131 is also shown. (C) Immunolocalization of dDEK on wild-type polytene chromosomes. The wild-type polytene chromosome squashes are costained with anti-dDEK (green) and anti-RNA polymerase II Ser5-P (as a maker of puff loci) antibodies (red) and DAPI (DNA stain, white). Endogenous dDEK is enriched at specific polytene chromosome sites, including ecdysone-induced puffs at 74EF and 75B (white box). The right panels present higher-magnification images of the white-boxed areas. (D) The distributions of dDEK (green) and H1 (as a marker of condensed chromatin, red) are shown in split images, including costaining for DNA (magenta). dDEK primarily associated with interband regions.