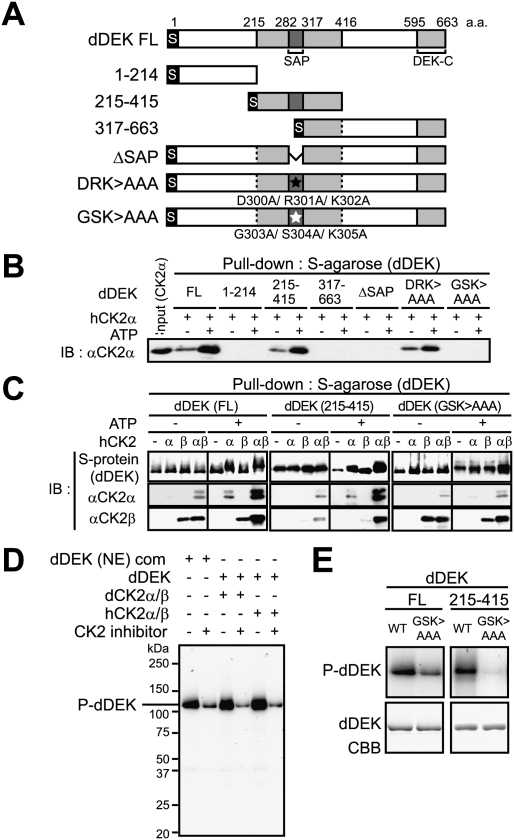
Figure 4.
CK2-mediated phosphorylation of dDEK regulates formation of the dDEK–CK2 complex. (A) Schematic representation of dDEK domain organization of full-length (FL) and mutant variants. The gray boxes represent the evolutionarily conserved region containing SAP (pfam 02037) or DEK-C (pfam 08766) domains. For each protein, the location of N-terminal S-tag is shown. Triple-alanine mutated residues are shown as closed asterisks (D300A/R301A/K302A; DRK > AAA) or opened asterisks (G303A/S304A/K305A; GSK > AAA). (B) Determination of the human CK2α subunit-binding region in dDEK. For pull-down assays, recombinant hCK2α (1 μg) was incubated with S-tagged dDEK (5 μg)-immobilized beads in the absence or presence of 100 μM ATP. The pull-downs were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-CK2α antibody. (C) Phosphorylation-dependent formation of the dDEK–hCK2 complex. Recombinant hCK2α (1 μg) and/or hCK2β (0.6 μg) proteins were pulled down by S-tagged FL and mutant dDEK proteins with or without ATP. Bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using indicated antibodies. (D, E) Phosphorylation of dDEK by CK2. In vitro kinase assays using 32P-γ-ATP were performed using purified dDEK (NE) complex or indicated recombinant proteins in the absence or presence of 5 μM DMAT as CK2 inhibitor (D), and dDEK mutant variants (E). The phosphorylated products were visualized by autoradiography.