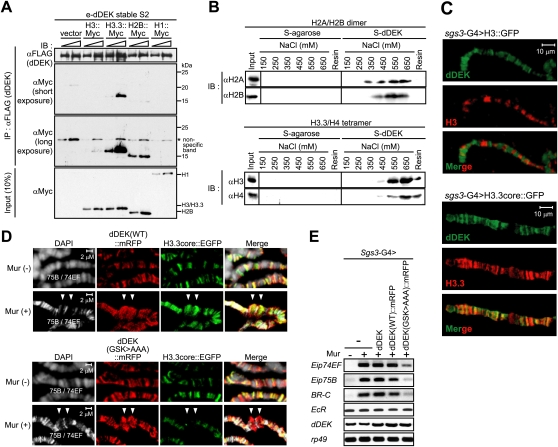
Figure 6.
The nucleosomal assembly activity of dDEK is required for ecdysone-inducible puff formation and EcR target gene expression. (A) Preferential association of dDEK with a histone variant, H3.3. Chromatin fractions from e-dDEK stable cells transfected with H3-myc, H3.3-myc, H2B-myc, or H1-myc were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag M2 resin. Each immunoprecipitated histone was detected using anti-Myc antibody. (B) Direct interaction of dDEK with histone H3.3/H4 tetramer. For pull-down assays, reconstituted recombinant Drosophila H2A/H2B dimer or H3.3/H4 tetramer were incubated with S-tagged dDEK protein immobilized on S-protein beads. Wash fractions (at each NaCl concentration) and final elution fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (C) Colocalization of dDEK with variant H3.3, but not canonical H3. Polytene chromosomes from larvae expressing H3∷EGFP (top) or H3.3core∷EGFP (bottom) fusion proteins driven by sgs3-GAL4 were coimmunostained with anti-dDEK (green) and anti-GFP (red) antibodies. (D) dDEK-dependent accumulation of H3.3 at ecdysone-inducible puff loci 74EF and 75B (arrowheads). The salivary glands from larvae coexpressing H3.3core∷EGFP (green) with dDEK(WT)∷mRFP or dDEK(GSK > AAA)∷mRFP (red) fusion proteins driven by sgs3-GAL4 were treated without or with Mur (2.5 × 10−7 M) as described in Figure 1C. The polytene chromosomes were subjected to immunostaining with anti-GFP and anti-RFP antibodies. (E) Abrogated expression of EcR-target genes in the fly line expressing dDEK defective in histone chaperone activity. RT–PCR was performed in RNA isolated from larval salivary glands expressing dDEK, dDEK(WT)∷mRFP, or dDEK(GSK > AAA)∷mRFP transgene. Semiquantitative RT–PCR analysis was performed as described in Figure 2C.