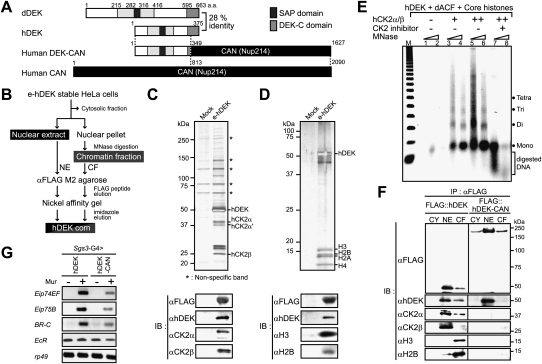
Figure 7.
Functional characteristics of hDEK and leukemia-associated fusion protein, DEK-CAN. (A) Schematic representation of dDEK, hDEK, hCAN, and hDEK-CAN fusion proteins (von Lindern et al. 1992). (B) The purification scheme for the hDEK-containing complex. (C,D) Mass spectrometric and Western blot analysis of the hDEK complex components purified from the NE (C) or chromatin fraction (D) in e-hDEK stable HeLa cells. Silver staining of the peak fraction of hDEK from the final Ni affinity purification step is shown in the top panels. MALDI-TOF/MS analysis of the complex subunits is shown on the right. Asterisks indicate background proteins. Purified hDEK complex fractions were used for Western blotting with the indicated antibodies in the bottom panels. (E) Histone chaperone activity of hDEK in vitro. Recombinant hDEK was subjected to the nucleosome assembly assay as described in Figure 5B. (F) Lack of functional components of hDEK complex in hDEK-CAN-overexpressing 293T cells. The cytosolic fraction (CY), NE, and chromatin fraction (CF) derived from 293T cells transiently transfected with Flag-tagged hDEK or hDEK-CAN were used for immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag M2 resin. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (G) Abrogated expression of EcR target genes in the fly line expressing hDEK-CAN leukemic fusion protein. RT–PCR was performed in RNA isolated from larval salivary glands expressing hDEK or hDEK-CAN. Semiquantitative RT–PCR analysis was performed as described in Figure 2C.