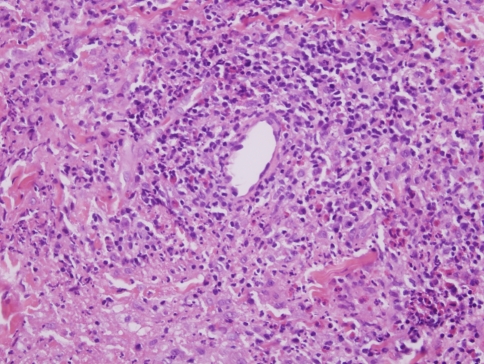
Fig. 1.
In early lesions of granuloma faciale a form of chronic leukocytoclastic vasculitis is observed. The hallmarks are nodular angiocentric mixed inflammatory cell infiltrates comprising lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils and plasma cells. There is vascular ectasia, focal mural fibrin deposition and some leukocytoclastic debris. As the process evolves, the degree of inflammation lessens and there is progressive angiocentric fibroplasia, which can eventuate into an obliterative fibrous tissue reaction