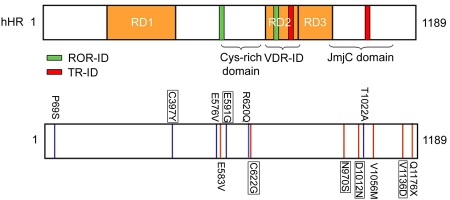
Figure 3. Mutant Hr alleles from human patients lack corepressor activity.
Naturally-occurring HR mutants tested for corepressor activity. Top, schematic representation of human HR protein (hHR) functional domains. Bottom, positions of mutated residues and altered amino acids. Blue indicates polymorphism, red indicates missense mutation. Mutants were tested for the ability to mediate repression by VDR and TR. Mutations in human HR were tested with VDR, mutants in rat HR (corresponding to the mutations found in human Hr alleles) were tested with TR (boxed). All proteins were expressed at equivalent levels except for P69S. All expressed proteins retain interaction with TR and VDR. In general, mutants lack corepressor activity, polymorphisms retain corepressor activity. Missense mutants (red): E583V (Paradisi et al., 2003); C622G/ C642G(rat) (Aita et al., 2000); N970S/N988S(rat) (Kruse et al., 1999); D1012N/D1030N(rat) (Klein et al., 2002); V1056M (Zlotogorski et al., 2002); V1136D/V1154D(rat) (Cichon et al., 1998), Q1176X (Henn et al., 2002). Polymorphisms (blue): P69S, C397Y/C422Y(rat), A576V, E591G/E611G(rat), R620Q, T1022A (Hillmer et al., 2002).