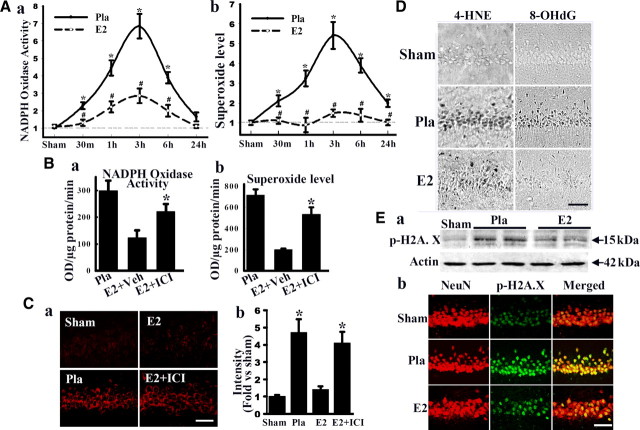
Figure 2.
E2 attenuates NADPH oxidase activity, superoxide production, and oxidative damage in hippocampal CA1 after global cerebral ischemia. A, Time course of NADPH oxidase activity (a) and superoxide production (b) in hippocampal CA1 region from sham, Pla-treated, and E2-treated rats. Values are means ± SE of four or five rats in each group and expressed as fold changed versus sham + Pla group. *p < 0.05 versus sham; #p < 0.05 versus Pla at the same time point. There was no difference between Pla + sham and E2 + sham groups. B, Effects of ICI182,780 (ICI) on NADPH oxidase activity (a) and superoxide production (b) in CA1 at 3 h after reperfusion. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle group. C, Representative pictures of oxidized HEt staining taken from medial CA1 region 3 h after reperfusion. Strong oxidized HEt staining was detected in Pla-treated and E2 + ICI182,780-treated brains after ischemia, whereas weak oxidized HEt signals were detected in sham and E2 groups (a). E2 significantly attenuated superoxide generation compared with Pla, which was reversed by ICI182,780 (b). *p < 0.01 versus sham and E2. D, Effect of E2 on oxidative damage markers for lipid peroxidation (4-HNE) and DNA damage (8-OHdG) 1 d after ischemia. Note that E2 strongly decreased 4-HNE and 8-OHdG staining. E, E2 markedly decreases levels of p-H2A.X in hippocampal CA1 neurons at 2 d after reperfusion as determined by Western blot analysis (a) and confocal immunohistochemical analysis (b). Scale bars, 50 μm. Magnification, 40×.