FIG. 1.
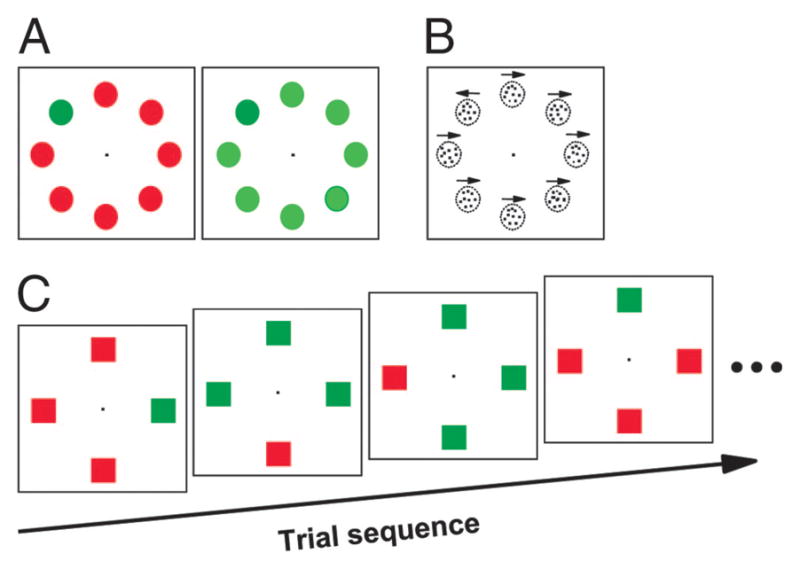
Visual search displays. Each trial began with the presentation of a fixation spot. After fixation for a variable interval a search array appeared. A: easy–hard color search. Stimuli were equiluminant, and the target–distractor similarity was manipulated by changing the color of the distractors. B: easy–hard motion search. Each stimulus was a circular aperture of randomly positioned dots. Direction of motion was either left or right. Motion of the target was opposite that of the distractors. Target–distractor similarity was manipulated by changing the proportion of dots moving coherently in all apertures. C: feature-switching task. Example sequence of 4 trials is shown. Monkeys’ task was to shift gaze to the popout oddball stimulus.
