Figure 3.
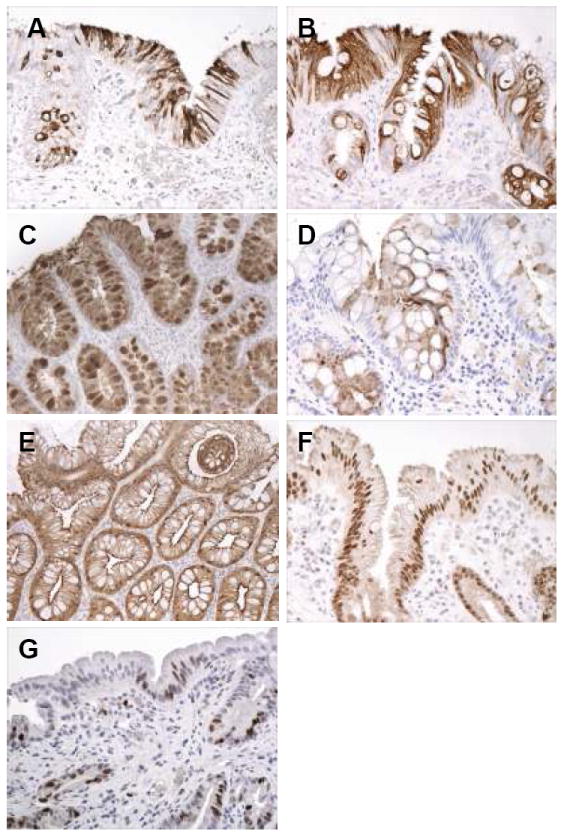
(A-G): Intestinal phenotypic markers and Ki67 staining in patients with Barrett’s esophagus, either low-density or high-density goblet cell subgroups. A. Strong cytoplasmic MUC2 staining in surface and crypt mucinous columnar cells, and in goblet cells, in this patient with columnar metaplasia of the esophagus with low-density goblet cells. B. Strong diffuse cytoplasmic staining in surface and crypt columnar cells, and goblet cells, in a patient with columnar metaplasia of the esophagus with high-density goblet cells. C. Strong MUC-5AC staining in columnar cells and goblet cells in this patient with high-density goblet cells. D. Cytoplasmic staining for DAS-1 in columnar cells and scattered goblet cells in this patient with columnar metaplasia of the esophagus with high-density goblet cells. E. Strong diffuse cytoplasmic staining in the surface and crypt epithelium for villin in this patient with high-density goblet cells. F. Nuclear staining for CDX2 in most cell nuclei in the surface and crypt epithelium in this patient with columnar metaplasia of the esophagus with low-density goblet cells. G. Nuclear staining for Ki67 in scattered surface columnar cells and crypt cells in this patient with columnar metaplasia of the esophagus and low-density goblet cells.
