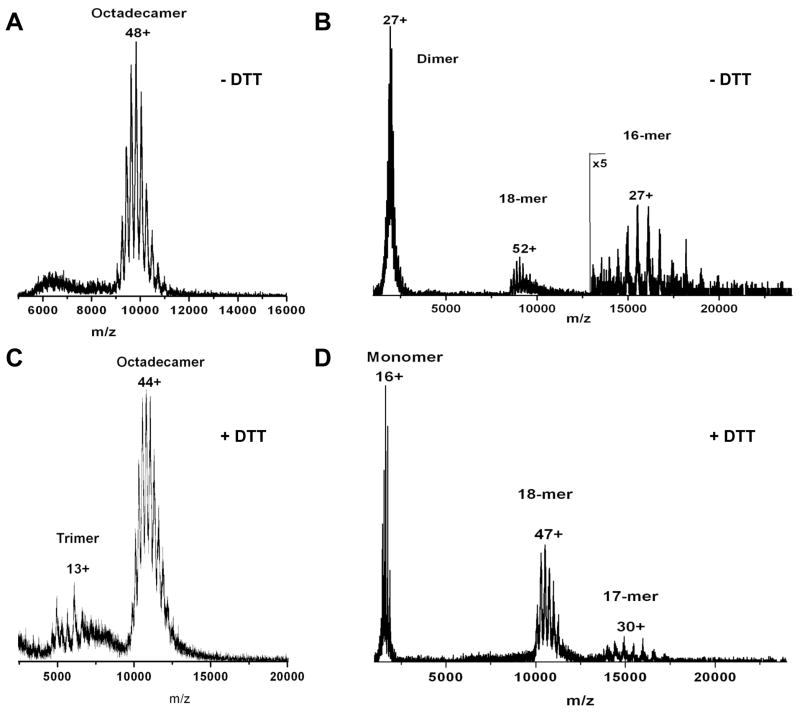
Figure 5. (A, C) Native and (B, D) collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of adiponectin octadecamers in the (A, B) absence or (C, D) presence of 1 mM DTT.
Purified bovine serum octadecamers in 200 mM ammonium acetate at pH 7 were treated with or without 1 mM DTT at 4°C overnight. Native and reduced adiponectin samples were ionized via nano-electrospray and their mass-to-charge ratios determined in a quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometer as described in Experimental Procedures. To assess the oxidation states of octadecameric adiponectin detected in the mass spectrometer, a single charged octadecamer species was selected by the quadrupole mass analyzer and fragmented by collision with argon gas. The mass-to-charge ratios of the fragments were determined in TOF and the charge state distributions were calculated using the MassLynx software system. The peaks corresponding to the monomers in the CID spectrum in panel D contain a predominant species with a molecular mass of 26206.7. As dimers consist of monomers with different posttranslational modifications, the peaks corresponding to the dimers in the CID spectrum in panel B are broader than those in panel D. The median molecular mass calculated from the range of dimer peaks is 52412.3.