Figure 4.
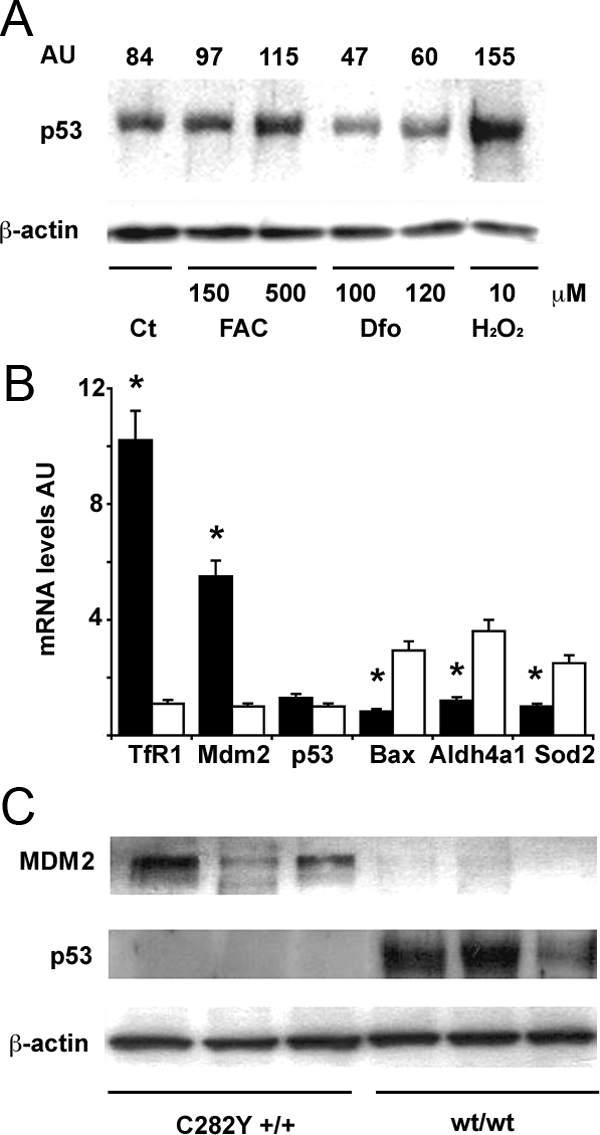
Effect of iron status on the MDM2/p53 pathway in human monocytes. A: Effect of iron status on p53 protein levels. Twenty-four hours after plating, after removal of lymphocytes, cells were treated as indicated for 24 hours. Ct: control, untreated monocytes. H2O2 is shown as positive control. β-actin is shown as a loading control. AU (arbitrary units): indicates the p53/β-actin ratio as detected by densitometry. Results are representative of two independent experiments. B: Expression of mRNAs of transferrin receptor-1 (up-regulated by iron depletion), MDM2, p53, and p53 target genes (including Bax, Aldh4a1, Sod2) in monocytes of subjects with C282Y +/+ HH (n = 6, black bars), and subjects with normal iron parameters negative for HFE mutations (n = 6, white bars). *P < 0.05 vs. control subjects. AU: mRNA levels, arbitrary units. C: MDM2 and p53 protein expression, as detected by Western blotting, in subjects with C282Y +/+ HH, and in subjects with normal iron parameters negative for HFE mutations. Three representative subjects are shown for each group. β-actin is shown as a loading control.
