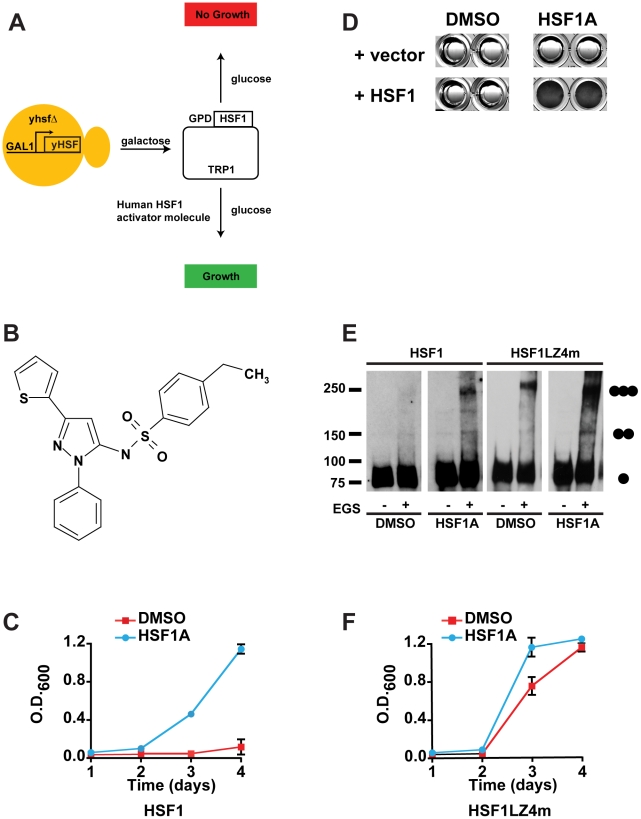
Figure 1. HSF1A activates human HSF1 function in yeast.
(A) Strategy used to identify chemical activators of human HSF1 in yeast. Yeast cells expressing the essential yeast HSF under control of the glucose-repressible GAL1 promoter are dependent on galactose for growth. Upon shifting cells to glucose-containing medium, the cells are dependent on activation of human HSF1 for growth. (B) Structure of HSF1A. (C) Yeast cells expressing wild-type human HSF1 were supplemented with 10 µM HSF1A or DMSO and grown in 96-well plates for 4 d. Growth was monitored by measuring OD600. (D) HSF1-dependence for HSF1A-mediated cell growth. Strain DNY75 expressing either human HSF1 (+HSF1) or an empty vector (+vector) were seeded into microtiter wells and incubated in the presence of HSF1A or DMSO solvent for 4 d and then photographed. Note that only cells expressing human HSF1 grow in response to HSF1A. (E) Yeast strain DNY75 was grown in the presence of DMSO or 20 µM HSF1A for 18 h, and HSF1 multimerization was evaluated by EGS cross-linking, SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotting. The positions of molecular weight markers are indicated on the left, and circles indicating the expected migration of HSF1 monomers, dimers, and trimers are on the right. (F) Yeast cells expressing HSF1LZ4m were supplemented with 10 µM HSF1A or DMSO and grown in 96-well plates for 4 d. Growth was monitored by measuring OD600.