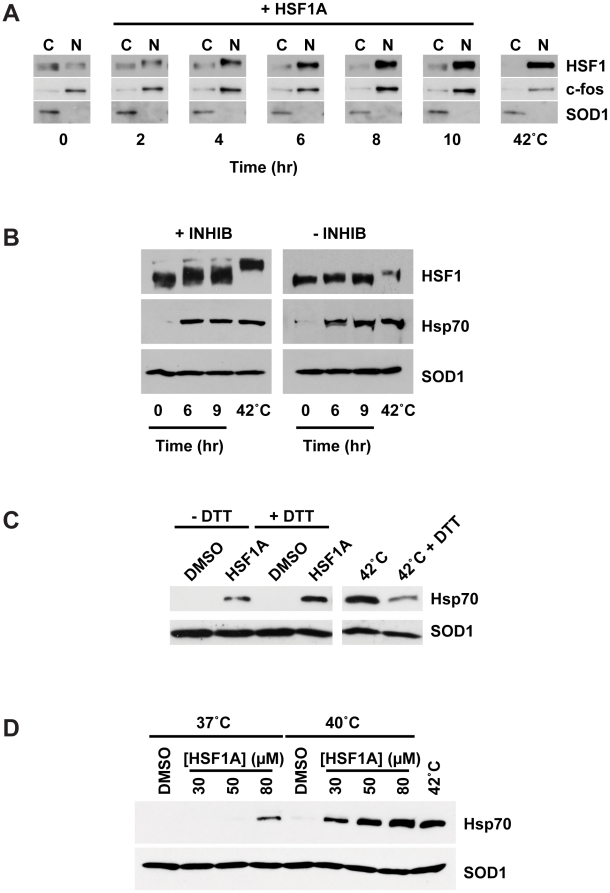
Figure 3. Features of HSF1A-dependent HSF1 activation.
(A) HSF1+/+ MEFs were treated with 80 µM HSF1A for the indicated time in hours or heat shocked at 42°C for 2 h, and nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were analyzed for HSF1 by immunoblotting. c-fos and SOD1 serve as nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) markers, respectively. (B) HSF1+/+ MEFs were treated with HSF1A for 6 h or 9 h or heat shocked at 42°C for 2 h in the presence (+) or absence (−) of phosphatase inhibitors (INHIB). (C) HSF1+/+ MEFs were pretreated with 250 µM DTT for 1 h prior to the addition of 80 µM HSF1A for 15 h or a 2-h heat shock at 42°C followed by a 15-h recovery. For comparison purposes, the heat-shocked samples are shown at a lower exposure than the HSF1A-treated samples. (D) HSF1+/+ MEFs were treated with either DMSO or HSF1A (30, 50, or 80 µM) for 15 h at 37°C. For synergistic activation of Hsp70 expression, wild-type MEFs were treated with either DMSO or HSF1A (30, 50, or 80 µM) for 1 h at 37°C prior to a 1-h heat shock at 40°C followed by a 15-h recovery period at 37°C. For control purposes, Hsp70 expression following a 1-h heat shock at 42°C, and a 15-h recovery is shown. SOD1 serves as the protein loading control.