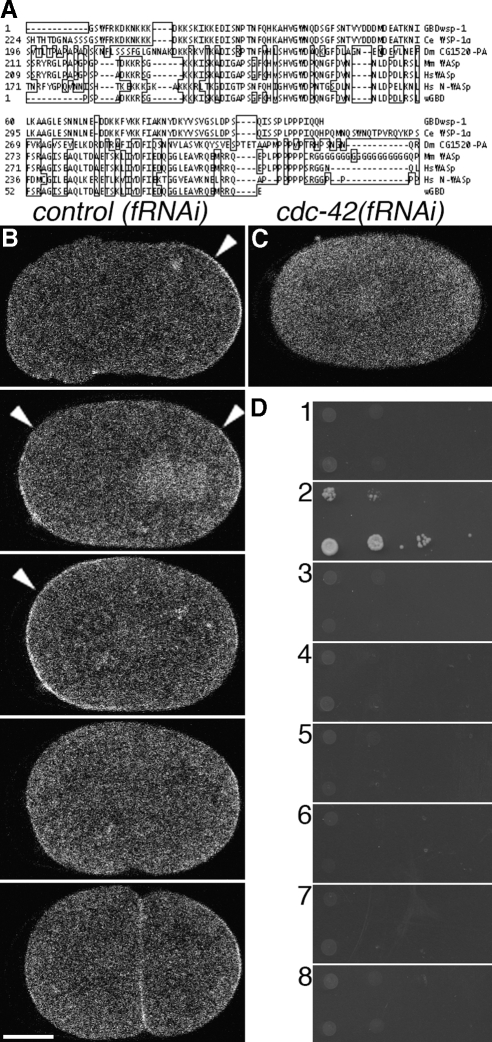
Figure 1.
Construction, validation, and localization of a biosensor of CDC-42 activity. (A) Alignment of identified GBDwsp-1 (top) with WSP-1 homologues of C. elegans, Drosophila, mouse and human (middle), and a probe that reports Cdc42 activity in Xenopus (bottom). Boxed amino acids are dissimilar to those of WSP-1. (B) Localization of GFP::GBDwsp-1 in a control(fRNAi) embryo. Arrowheads indicate polarized enrichment of cortical signal. From top to bottom: phase I, transition from phase I to phase II, phase II, phase III, completion of cytokinesis. (C) Localization of GFP::GBDwsp-1 in a cdc-42(fRNAi) embryo. (D) Yeast two-hybrid showing interaction between GBDwsp-1 and (2) the active CDC-42(Q61L) mutant but not (1) the inactive CDC-42(T17N) mutant, (3) the inactive CED-10(T17N) mutant, (4) the active CED-10(Q61L) mutant, (5) the inactive RHO-1(T19N) mutant, (6) the active RHO-1(Q63L) mutant, or (7) empty-vector control. (8) There is no interaction between the paired empty-vector controls. In these (and all subsequent) micrographs of embryos, the embryo is positioned with anterior to the left and posterior to the right. Bar, 10 μm.